Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
H
H
N
C-17
N
C-17
N
N
O
H
N
O
H
N
r
4
r
4
O
O
H
r
5
H
q
5
q
4
q
4
H
H
H
N
r
6
N
N
N
N
O
H
N
H
N
G-5
A-5
q
6
A-14
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
G5A,
no activity
WT,
k
rel
= 1
H
H
C-17
N
C-17
N
N
N
O
H
N
O
H
N
r
4
r
4
O
O
r
5
q
4
q
4
H
H
H
q
5
H
H
N
N
O
N
N
N
r
6
H
H
N
I-5
N
D-5
q
6
N
A-14
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
G5D,
k
rel
»
10
-
4
G5I,
k
rel
»
1
´
10
-
3
to 6
´
10
-
3
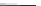
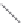
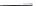
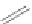
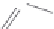
Figure 2.12 Schematic representations of the mutants of the G5 position and the
hydrogen bonding network between the G5 and C17 positions. k
rel
is the experimental
cleavage constant relative to the wild type. The relevant references are listed in
Table 2.13
.
phosphorane and phosphodiester bond cleavage. The p
K
a
of the general acid
is believed to be shifted toward neutrality through interaction of a divalent
metal ion that bridges the phosphoryl oxygens of A9 and the scissile phos-
phate. These oxygens are positioned approximately 4.3
˚
away from one
another in the crystal structure, and both exhibit significant catalytic thio
effects in the presence of Mg
2
þ
ions that can be rescued by titration with
thiophilic Cd
2
þ
ions. Simulation results indicate that the divalent metal
ion migrates from a distal binding site involving A9 and G10 in the reactant
state to a bridging position between A9 and scissile phosphates upon forma-
tion of the activated precursor.



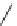













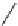





































































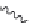



















































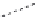


















Search WWH ::

Custom Search