Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
HHR. A preliminary communication of these results has been presented
elsewhere.
79
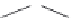
The reaction mechanisms considered here, (see
Fig. 2.4
) assume that the
2
0
OH group of C17 has already been activated (i.e., deprotonated) and act as a
nucleophile to undergo in-line attack on the adjacent scissile phosphate, pass-
ing through a pentavalent phosphorane intermediate/transition state,
followed by acid-catalyzed departure of the O5
0
leaving group of C1.1.
The general acid is assumed to be the 2
0
OH group of G8. The goal of the
work is to provide insight into two fundamental questions regarding the cat-
alytic mechanism: (1) to characterize and quantify the degree to which the
phosphoryl transfer step and general acid step are coupled (i.e., occur via a
stepwise or a concerted mechanism) and (2) to identify and quantify the spe-
cific role of a key divalent metal ion in each chemical step of the reaction.
In order to answer these questions, we have determined a minimum
free-energy reaction pathway by simulating a series of six two-dimensional
(2D) potential of mean force (PMF) or free-energy profiles, and 1D PMF
refinements along the minimum free-energy paths (MFEPs) that require
an aggregate of over 100 ns of QM/MM simulation.
3.1. Results
3.1.1 Phosphoryl transfer and general acid steps follow a stepwise
mechanism and depend on Mg
2þ
coordination
Our initial attempts to study the chemical steps of the HHR reaction from
2D PMF profiles using phosphoryl transfer and proton transfer reaction
coordinates, but not considering a reaction coordinate associated with
Mg
2
þ
ion-binding mode,
led to barriers that were unexpectedly high
(
37 kcal/mol). We extended the calculations so as to include 3D-PMF
profiles with a coarse-grained reaction coordinate associated with the
C17
C17
C17
C17
C17
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
2
O
O
2
O
O
O
2
O
2
O
O
2
O
P
P
O
P
P
O
P
O
O
O
O
O
5
O
O
O
Mg
2+
Mg
2+
O
5
Mg
2+
OH
C1.1
O
5
Mg
2+
O
5
Mg
2+
H
C1.1
H
O
2
O
2
H
O
2
O
2
C1.1
C1.1
C1.1
H
O
2
G8
G8
G8
G8
G8
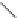
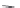
Figure 2.4 The proposed HHR reaction pathway derived from the free-energy profiles
obtained in
Section 3.1
.











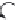










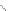












































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search