Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
2.7. Cleavage and ligation reactions in the hairpin
ribozyme
the internal equilibrium
The four-way helical junction of the hairpin ribozyme is conformationally
predisposed to fold into the conformer that juxtaposes the loops of the A and
B arms,
28,31
allowing the ribozyme to fold in physiological ionic condi-
tions.
11-13,31,69-71
It also promotes the ligation reaction.
72
FRET has been
used to follow the cleavage and ligation reactions in the individual hairpin
ribozyme.
73
Single ribozyme molecules can be observed switching between
two distinct dynamic modes (
Fig. 3.8
). In one state (assigned as the ligated
species), the molecule remains stably docked for a period before changing
into another form (assigned as the cleaved form) that undergoes rapid dock-
ing and undocking. The docking and undocking rates within the cleaved
—
cleave
undock
ligate
dock
cle
lig
cle
lig
cle
lig
1.0
0.5
0
0
20
40
60
80
100
Time / s
Figure 3.8 Cleavage and ligation reactions observed in single hairpin ribozyme mole-
cules.
73
Junction-form hairpin ribozymes fluorescently labeled at the termini of the
A and B arms were tethered to the surface of a quartz slide, and FRET between donor
and acceptor was measured from individual ribozyme molecules over a period of time.
FRET efficiency is plotted as a function of time for one molecule. The molecule can be
seen to switch between two states. In one state (assigned as the ligated form), the mol-
ecule is stably folded into a structure that places the fluorophores close together (and
hence high FRET efficiency E
FRET
is observed). In another state (assigned as the cleaved
state), there is rapid oscillation between a docked state (high E
FRET
) and a more
extended structure where the loops are not associated (low E
FRET
). The interpretation
is shown by the schematic above the time trace. The transition from stable to oscillat-
ing states is deduced to be a cleavage event (cle), and the transition from oscillating to
stable states is assigned as a ligation event (lig). From the duration of the ligated and
cleaved states, the kinetics of cleavage and ligation reactions can be calculated.

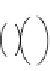



















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search