Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
strategy requires that the acid be protonated and the base unprotonated at the
outset of the reaction. The observed rate of reaction (
k
obs
) will be given by
k
obs
¼
k
cat
f
A
f
B
where
f
A
and
f
B
are the fractions of protonated acid and unprotonated base,
respectively, and
k
cat
is the rate of cleavage catalyzed by the ribozyme in the
requisite state of protonation and is independent of pH.
f
A
and
f
B
can be
calculated for any pH if p
K
a
values are assumed, and thus the pH dependence
of cleavage rate can be simulated.
61
We reinvestigated the pH dependence of
the cleavage reaction in the presence of a high concentration of Mg
2
þ
ions,
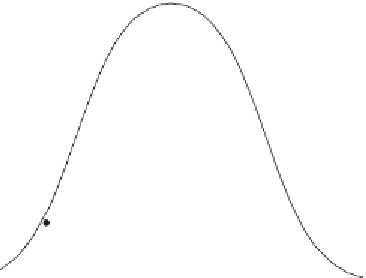
and obtained a bell-shaped pH dependence (
Fig. 3.6
), which was fitted to a
double-ionization model with apparent p
K
a
values of 5.2 and 8.4.
22
The
lower value is very much in agreement with an adenine in an electronegative
environment, while the upper value is consistent with a guanine base if the
p
K
a
were reduced by proximity to metal ions. Using the fast-cleaving
cis
-
acting form of the ribozyme, Smith and Collins
62
also obtained a bell-shaped
pH dependence for cleavage, with p
K
a
values of 5.8 and 8.3.
We have carried out a detailed analysis of pH effects for position 638
using the
trans
cleavage reaction. A G638I substrate produced a bell-shaped
8
7
6
5
k
obs
/ min
-
1
4
3
2
1
0
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
pH
Figure 3.6 pH dependence of the rate of substrate cleavage by the VS ribozyme.
22
The
data have been fitted to a double-ionization model.

































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search