Java Reference
In-Depth Information
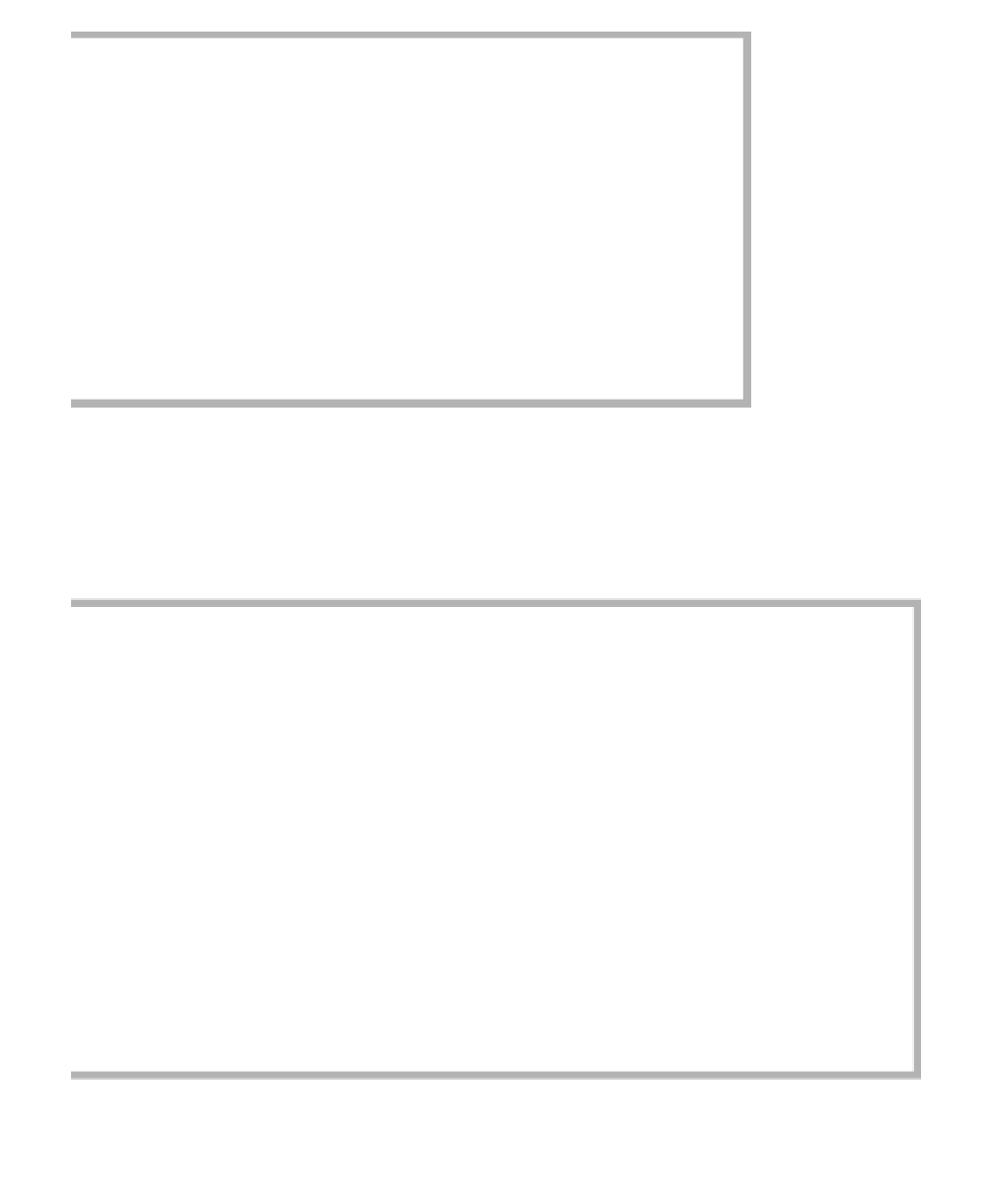
1
/**
2
* Removes an item from this collection.
3
* @param x any object.
4
* @return true if this item was removed from the collection.
5
*/
6
public boolean remove( Object x )
7
{
8
Node<AnyType> pos = findPos( x );
9
10
if( pos == NOT_FOUND )
11
return false;
12
else
13
{
14
remove( pos );
15
return true;
16
}
17
}
figure 17.28
Additional
remove
method for standard
LinkedList
class
The iterator factories are shown in Figure 17.29. Both return a freshly
constructed
LinkedListIterator
object. Finally, the
LinkedListIterator
, which
is perhaps the trickiest part of the whole implementation, is shown in
Figure 17.30.
1
/**
2
* Obtains an Iterator object used to traverse the collection.
3
* @return an iterator positioned prior to the first element.
4
*/
5
public Iterator<AnyType> iterator( )
6
{
7
return new LinkedListIterator( 0 );
8
}
9
10
/**
11
* Obtains a ListIterator object used to traverse the
12
* collection bidirectionally.
13
* @return an iterator positioned prior to the requested element.
14
* @param idx the index to start the iterator. Use size() to do
15
* complete reverse traversal. Use 0 to do complete forward traversal.
16
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if idx is not
17
* between 0 and size(), inclusive.
18
*/
19
public ListIterator<AnyType> listIterator( int idx )
20
{
21
return new LinkedListIterator( idx );
22
}
figure 17.29
Iterator factory methods for standard
LinkedList
class
Search WWH ::

Custom Search