Java Reference
In-Depth Information
1
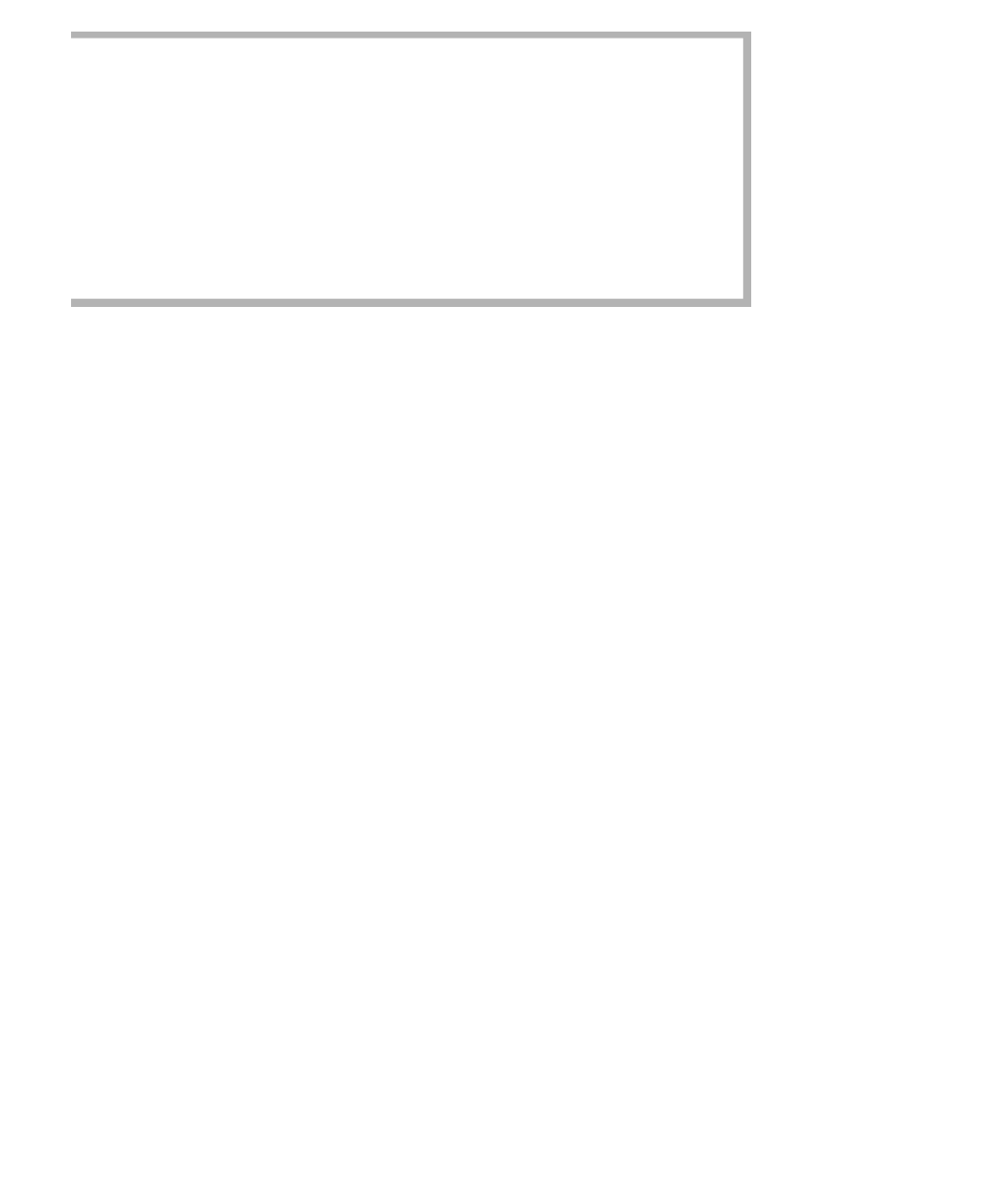
public void clear( ) // Version #1
2
{
3
Iterator<AnyType> itr = iterator( );
4
figure 15.18
Proposed
implementations of
clear
for
AbstractCollection
while( !isEmpty( ) )
remove( itr.next( ) );
5
6
}
7
8
public void clear( ) // Version #2
9
{
10
while( !isEmpty( ) )
remove( iterator( ).next( ) );
11
12
}
Figure 15.18 contains two proposed implementations of
clear
for
AbstractCollection
. Does either work?
15.10
PROGRAMMING PROJECTS
15.11
The
Collection
interface in the Java Collections API defines methods
removeAll
,
addAll
, and
containsAll
. Add these methods to the
Collection
interface and provide implementations in
AbstractCollection
.
15.12
Collections.unmodifiableCollection
takes a
Collection
and returns an
immutable
Collection
. Implement this method. To do so, you will need
to use a local class (a class inside a method). The class implements the
Collection
interface and throws an
UnsupportedOperationException
for
all mutating methods. For other methods, it forwards the request to the
Collection
being wrapped. You will also have to hide an unmodifiable
iterator.
Two
Collection
objects are equal if either both implement the
List
inter-
face and contain the same items in the same order or both implement the
Set
interface and contain the same items in any order. Otherwise, the
Collection
objects are not equal. Provide, in
AbstractCollection
, an
implementation of
equals
that follows this general contract. Addition-
ally, provide a
hashCode
method in
AbstractCollection
that follows the
general contract of
hashCode
. (Do this by using an iterator and adding the
hashCode
s of all the entries. Watch out for
null
entries.)
15.13
Search WWH ::

Custom Search