Java Reference
In-Depth Information
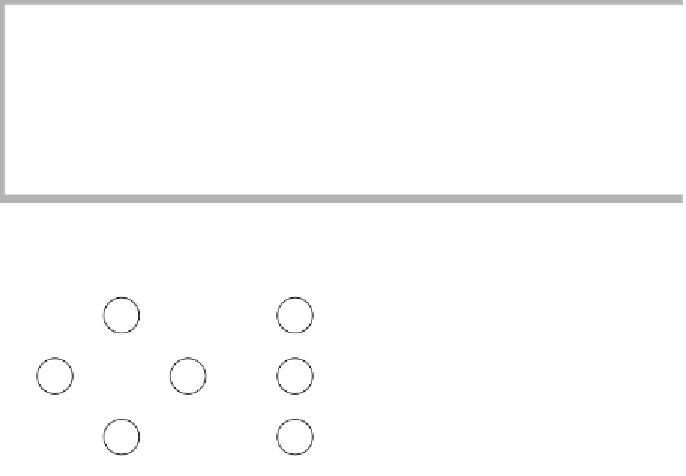
figure 14.36
Latest completion
times
C
3
0
0
0
0
F
3
2
4
7d
7
0
0
3
6
6
9
A
3
D
2
G
2
H
1
0
1
6d
6
8d
8
10d
10
B
2
0
4
6
9
9
10
7
0
0
E
1
K
4
3
5
9
4
5
9
figure 14.37
Earliest completion
time, latest
completion time, and
slack (additional edge
item)
3
6
6
9
C
3 0
F
3 0
0
0
0
0
2
4
7d
7
0
0
3
6
9
6
0
3
9
10
5
5
7
A
3 0
H
1 0
D
2 1
G
2 2
0
1
6d
6
8d
8
10d
10
B
2 2
0
4
6
7
9
9
10
2
3
7
0
0
E
1 2
K
4 2
3
5
9
4
5
9
Slack time
is the
amount of time that
an activity can be
delayed without
delaying overall
completion.
The
slack time
for each edge in the event-node graph is the amount of
time that the completion of the corresponding activity can be delayed without
delaying the overall completion, or
Slack
(
v, w
)
=
LC
w
-
EC
v
-
c
v, w
Figure 14.37 shows the slack (as the third entry) for each activity in the event-
node graph. For each node, the top number is the earliest completion time and
the bottom number is the latest completion time.
Some activities have zero slack. These are critical activities that must be fin-
ished on schedule. A path consisting entirely of zero-slack edges is a
critical path.
Zero-slack activi-
ties are critical and
cannot be delayed.
A path of zero-
slack edges is a
critical path.
In this chapter we showed how graphs can be used to model many real-life
problems and in particular how to calculate the shortest path under a wide
variety of circumstances. Many of the graphs that occur are typically very



































Search WWH ::

Custom Search