Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
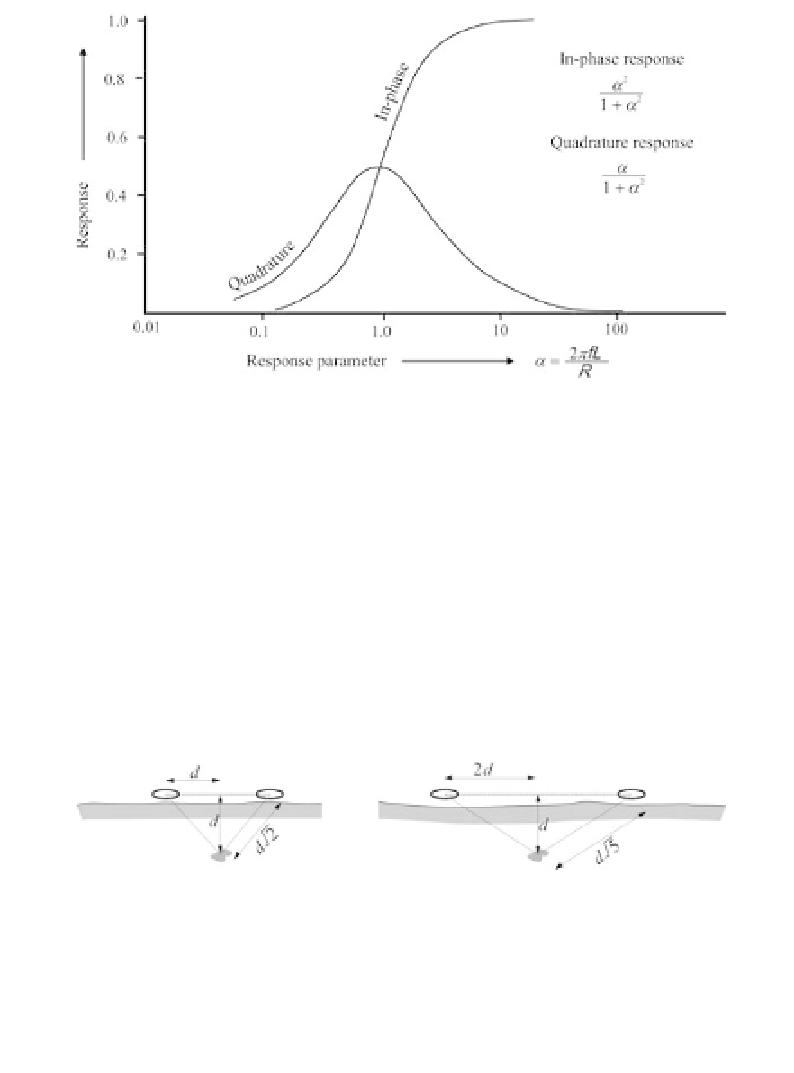
Figure 8.2
Response of a horizontal-loop electromagnetic (EM) system to a
vertical loop target, as a function of the response parameter (
α
).
L
is the loop
self-inductance,
R
its resistance and
f
is the frequency. Note that the fre-
quency scale is logarithmic. Curves for more complex targets have the
same general form, and in-phase/quadrature ratios can therefore be used
qualitatively as guides to conductivity.
8.1.4 Slingram practicalities
The coil separation in a Slingram survey should be adjusted to the desired
depth of penetration. The greater the separation, the greater the effective
penetration, because the primary field coupling (
M
tr
) is reduced more by
the increase than is either
M
ts
or
M
sr
(Figure 8.3). The maximum depth of
Figure 8.3
Spacing and penetration. When the two coils are moved apart,
the fractional change in distance between them is greater than between
either and the conductor at depth. The increased separation thus increases
the anomalous field as a percentage of the primary. In the example, in which
the coil separation is initially equal to twice the depth of the conducting
body, doubling the coil separation increases the coil to target distances by
only about 60%.