Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
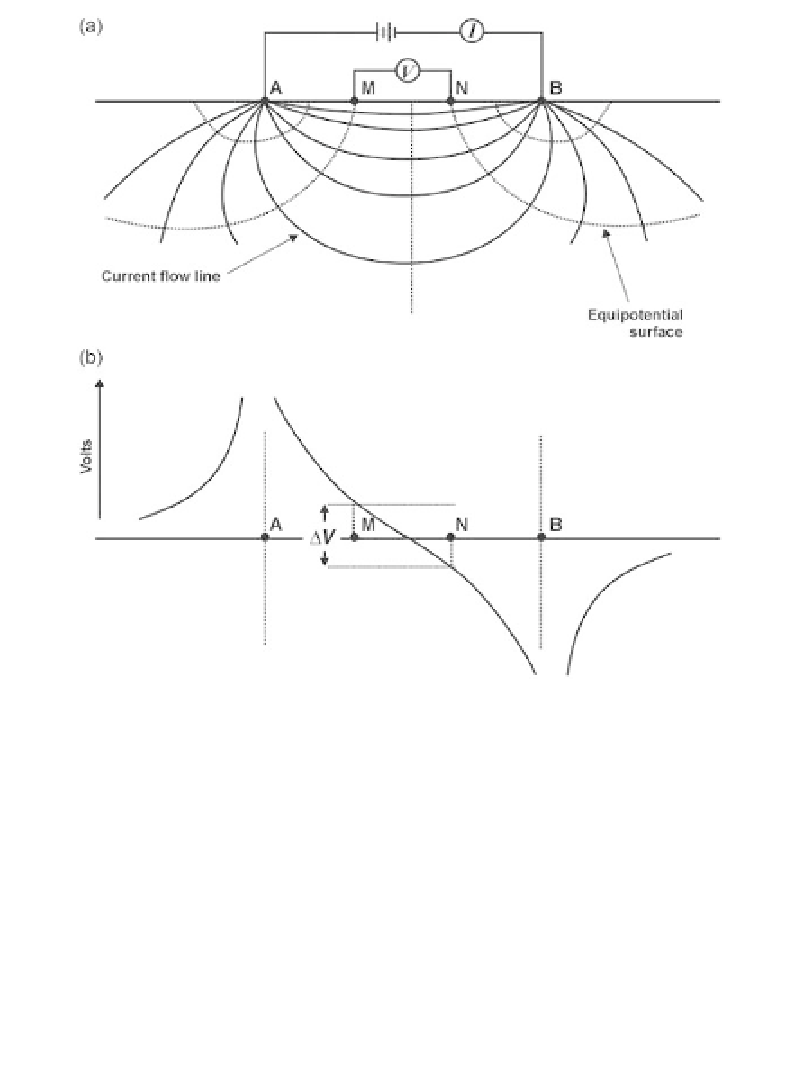
Figure 6.1
(a) Current flow (continuous lines) between electrodes A and B
and equipotential surfaces (dotted lines, orthogonal to the current lines) in
a homogeneous half-space. (b) Voltage drops. The potential
Vismeasured
between the electrodes M and N, positioned (in this case) as for a Wenner
array.
which defines the electric potential at a distance
a
from a point electrode
at the surface of a
uniform half-space
(homogeneous ground) of resistivity
ρ
. The current
I
may be positive (if into the ground) or negative, and the
potential at any point is equal to the sum of the contributions from the
individual current electrodes.
The difference between the summed potentials at the two voltage elec-
trodes M and N is equal to:
V
=
I
ρ/
2
π
(1
/
[MA]
−
1
/
[NA]
−
1
/
[MB]
+
1
/
[NB])