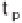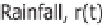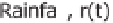Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
Infiltration
capacity,f(t)
(b)
(c)
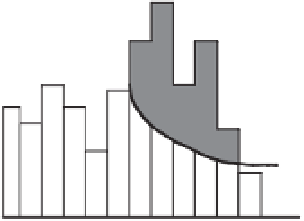
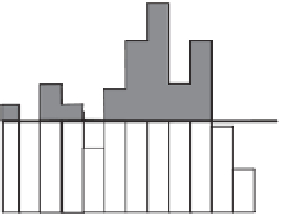
Figure 2.4
Methods of calculating an effective rainfall (shaded area in each case): (a) when rainfall intensity
is higher than the infiltration capacity of the soil, taking account of the time to ponding if necessary; (b) when
rainfall intensity is higher than some constant “loss rate” (the index method); (c) when effective rainfall is a
constant proportion of the rainfall intensity at each time step.
a sequence of rainfalls and a separated storm hydrograph, once a unit hydrograph is available for a
catchment, it can be used in an inverse way to estimate a pattern of effective rainfall. Indeed, by using
an iterative process starting with some initial estimate of the form of the unit hydrograph, both effective
rainfall sequences and the unit hydrograph can be calibrated without making any assumptions about the
nature of the runoff generation processes (see Box 4.2). Unfortunately, this does not appear to make it