Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
tar sand deposits. Then, depending on the method, either steam, hot water, pressurized air
either in an extraction plant (to which the sands are transported using giant strip-mining
machines) or in the ground (known as in situ extraction).
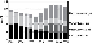
Figure 6.7.
U.S. oil and gas production over the last thirty years and projection to 2035
(in million barrels of oil equivalent per day). This surge in unconventional resources will
have implications well beyond the United States.
Source:
IEA (
2012a
) (modified).
The water and sludge that are left over from tar sand extraction, containing high levels
of heavy metals and chemicals known as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), are
stored in tailing ponds, which may leak. The levels of PAHs recently found in Alberta's
lakes are two to twenty times higher than before tar sand mining began. PAHs and heavy
metals are known to cause cancer and other health problems in animals and humans.
According to Peter Hodson, a biologist at Queen's University in Ontario, “hydrocarbon
pollution in the Athabasca River watershed is entirely caused by natural erosion of bitumen
and is no longer tenable” (Biello
2013c
).
Additionally, oil from tar sands is amongst the most greenhouse-gas-intensive forms of
petroleum. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency estimates that life cycle emissions
from tar sands are about 80 percent greater than the emissions from crude oil. According
to the renowned climatologist James Hansen, using resources such as tar sands will mean