Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
(g)
(h)
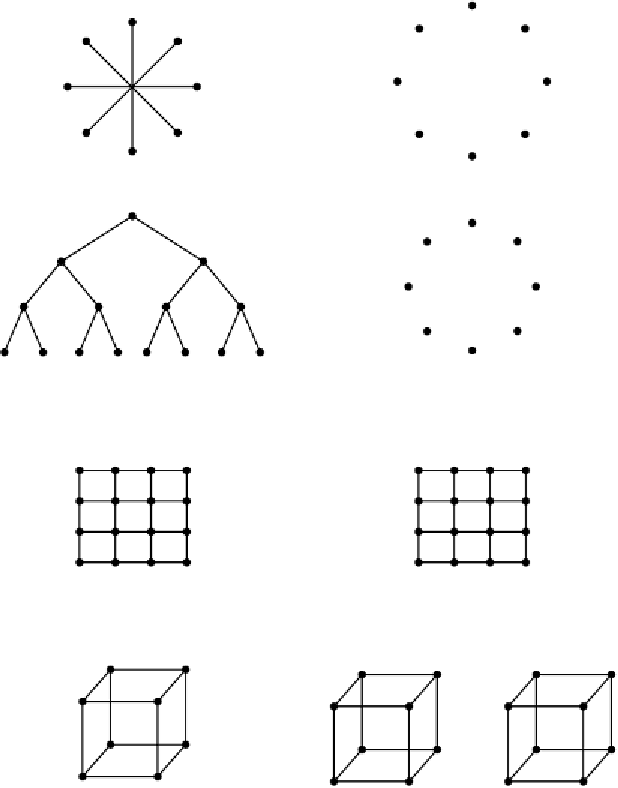
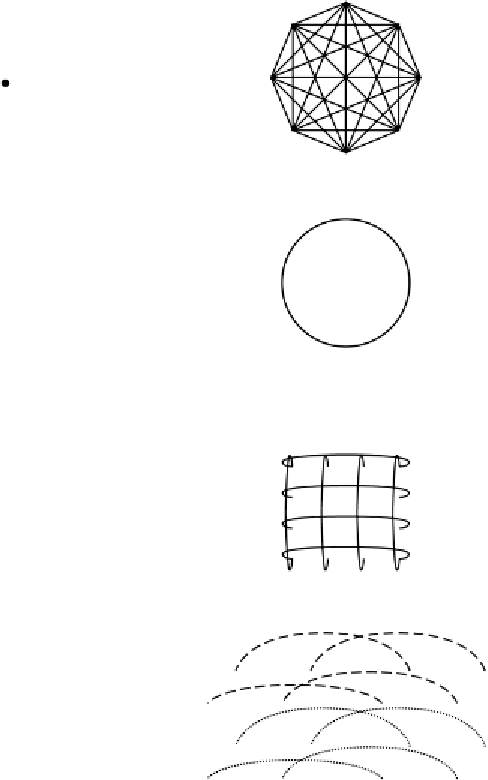
Figure 8-37.
Various topologies. The heavy dots represent switches. The CPUs
and memories are not shown. (a) A star. (b) A complete interconnect. (c) A tree.
(d) A ring. (e) A grid. (f) A double torus. (g) A cube. (h) A 4D hypercube.
Interconnection networks can be characterized by their
dimensionality
.For
our purposes, the dimensionality is determined by the number of choices there are
to get from the source to the destination. If there is never any choice (i.e., there is
only one path from each source to each destination), the network is zero dimen-
sional. If there is one dimension in which a choice can be made, for example, go