Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
Quick Path Interconnect (QPI) port. The QPI port connects the processor to an ex-
ternal multiprocessor interconnect, allowing systems with more than six processors
to be built. The QPI port sends and receives cache coherency requests, plus a varie-
ty of other multiprocessor management messages such as interprocessor interrupts.
A problem with the Core i7 as well as with most other modern desktop-class
CPUs, is the power it consumes and the heat it generates. To prevent damaging the
silicon, the heat must be moved away from the processor die soon after it is pro-
duced. The Core i7 consumes between 17 and 150 watts, depending on the fre-
quency and model. Consequently, Intel is constantly searching for ways to manage
the heat produced by its CPU chips. Cooling technologies and heat-conductive
packaging are vital to protecting the silicon from burning up.
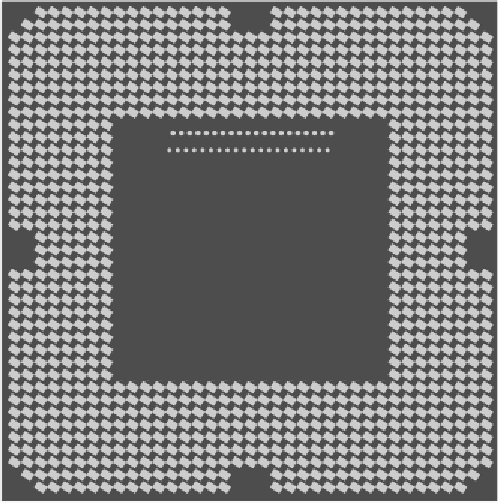
The Core i7 comes in a square LGA package 37.5 mm on edge. It contains
1155 pads on the bottom, of which 286 are for power and 360 are grounded to re-
duce noise. The pads are arranged roughly as a 40
×
40 square, with the middle 17
×
25 missing. In addition, 20 more pads are missing at the perimeter in an asym-
metric pattern, to prevent the chip from being inserted incorrectly in its socket.
The physical pinout is shown in Fig. 3-44.
Figure 3-44.
The Core i7 physical pinout.
The chip is outfitted with a mounting plate for a heat sink to distribute the heat
and a fan to cool it. To get some idea of how large the power problem is, turn on a