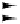Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
Addressing
Bus arbitration
Data
Coprocessor
Typical
Micro-
Processor
Bus control
Status
Interrupts
Miscellaneous
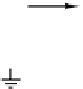
Symbol for
electrical ground
Φ
Power
Symbol
for clock
signal
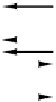
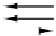
Figure 3-34.
The logical pinout of a generic CPU. The arrows indicate input
signals and output signals. The short diagonal lines indicate that multiple pins
are used. For a specific CPU, a number will be given to tell how many.
other activity, while the I/O device is doing its work. When the I/O has been com-
pleted, the I/O controller chip asserts a signal on one of these pins to interrupt the
CPU and have it service the I/O device, for example to check whether if I/O errors
occurred. Some CPUs have an output pin to acknowledge the interrupt signal.
The bus arbitration pins are needed to regulate traffic on the bus, in order to
prevent two devices from trying to use it at the same time. For arbitration pur-
poses, the CPU counts as a device and has to request the bus like any other device.
Some CPU chips are designed to operate with coprocessors such as float-
ing-point chips, but sometimes graphics or other chips as well. To facilitate com-
munication between CPU and coprocessor, special pins are provided for making
and granting various requests.
In addition to these signals, there are various miscellaneous pins that some
CPUs have. Some of these provide or accept status information, others are useful
for debugging or resetting the computer, and still others are present to assure com-
patibility with older I/O chips.
A
bus
is a common electrical pathway between multiple devices. Buses can be
categorized by their function. They can be used internal to the CPU to transport
data to and from the ALU, or external to the CPU to connect it to memory or to I/O
devices. Each type of bus has its own requirements and properties. In this section
and the following ones, we will focus on buses that connect the CPU to the memo-
ry and I/O devices. In the next chapter we will examine more closely the buses in-
side the CPU.