Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
their true values and the flow injections calculated from these pressures create imbal-
ances in each node. Thus, the nodal flow imbalances are a function of all the nodal
pressures in the system. These nodal flow errors will be reduced to a small quantity
(
e.g.
1e-10) as the pressure variables approach their true values. Once a solution is
reached, important and reliable steady-state operational data can be obtained. If the
load flow is done for multiple periods, then multiple snap shots of how the system
performs can be determined.
Weymouth's flow equation stands out in the literature since it can be applied for
high-, medium- and low-pressure networks. In addition, the equation for the friction
factor is only length and diameter dependent, measured respectively, in metres and
millimetres. These attributes greatly simplify the interactions between pipe and fluid
since they do not consider factors such as elevation and temperature.
The friction factor of the pipe element uniting nodes
k
and
m
can be detailed
as [171]:
10
3
L
km
D
km
K
km
=
11
.
7
×
(3.35)
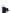
Analogous to Figure 3.2, Figure 3.4 describes a three-node natural gas net-
work which is used as a basis to develop the nodal equations of the system. The
considerations taken to build the incidence matrix for this particular system are:
Node
k
is the source and reference node, having a fixed pressure value and
therefore independent of the demand;
●
F
k
,
F
l
and
F
m
are the net nodal injections, respectively, at nodes
k
,
l
and
m
;
●
The nodal flows are composed from multiple elements but not shown for
simplicity purposes.
●
Gas flows are unidirectional and in order to move from one point to another there
needs to be a pressure drop between the connecting nodes. Thus, the pressure drop is
calculated in terms of the flow going through the pipe and its corresponding friction
coefficient.
k
l
K
kl
F
kl
F
k
F
l
F
km
F
lm
K
km
K
lm
m
F
m
Figure 3.4
Natural gas test network employed to develop the incidence matrix
















Search WWH ::

Custom Search