Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
q
2
ψ
(
τ
)
q
1
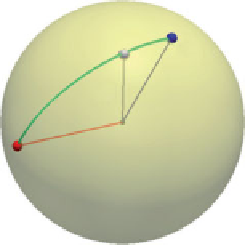
Figure 3.8
Illustration of shape space and geodesic between its elements
two points in
C
. Since
C
is a sphere, the geodesic length between any two points
q
1
,
q
2
∈
C
is
given by
cos
−
1
(
d
c
(
q
1
,
q
2
)
=
q
1
,
q
2
)
,
(3.7)
and the geodesic path
ψ
:[0
,
1]
→
C
,isgivenby
1
sin(
ψ
(
τ
)
=
)
(sin((1
−
τ
)
θ
)
q
1
+
sin(
θτ
)
q
2
)
,
θ
where
and geodesic path between two elements
of that space. As illustrated in Figure 3.8, the space of all curves is a sphere in Hilbert space.
Thus, the geodesic on the space of curves is the arc of the great circle connecting the two
curves seen as elements of this sphere.
It is easy to see that several elements of
θ
=
d
c
(
q
1
,
q
2
). Figure 3.8 illustrates the space
C
C
can represent curves with the same shape. For
3
, and thus its facial curves, we get different SRVFs for the
curves but their shapes remain unchanged. Another similar situation arises when a curve is
reparametrized; a reparametrization changes the SRVF of curve but not its shape. In order to
handle this variability, we define orbits of the rotation group
SO
(3) and the reparametrization
group
example, if we rotate a face in
R
as equivalence classes in
C
. Here,
is the set of all orientation-preserving diffeomor-
phisms of
I
(to itself) and the elements of
are viewed as reparametrization functions. For
β
→ R
3
and a function
γ
∈
β
◦
γ
example, for a curve
:
I
, the curve
is a reparametrization
→
√
˙
β
γ
γ
of
. The corresponding SRVF changes according to
q
(
t
)
(
t
)
q
(
(
t
)). We define the
equivalent class containing
q
as
˙
[
q
]
={
γ
(
t
)
Oq
(
γ
(
t
))
|
O
∈
SO
(3)
,γ
∈
}
.
3
The set of such equivalence class is called
shape space
of open curves in
R
denoted by
=
C/
S
(
SO
(3)
×
). Thanks to SRV representation, the groups
×
SO
(3) act by isometries.
This is a necessary condition to let the quotient space
S
inherits the Riemannian metric from
the preshape space
, one
needs to solve the optimization problem, which is typically done using dynamic programming.
C
. To obtain geodesics and geodesic distances between elements of
S