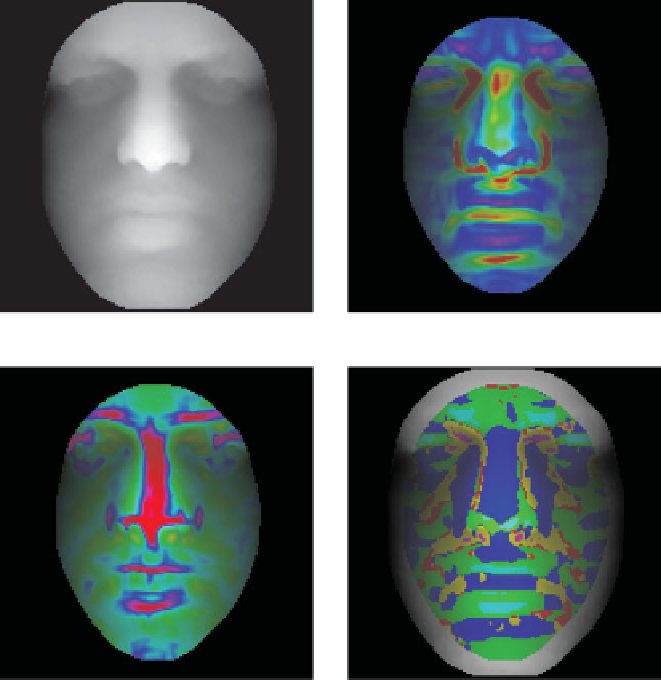
Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Figure 2.4
(a) A range image of a neutral face and its maximum and minimum principal curvatures,
(b), and (c). The red color indicates higher curvatures while the blue color indicates lower curvatures.
The image (d) shows the segmented local patches of the facial surface over-laid on the range image. The
color codes are red for planar regions, yellow for valleys, green for ridges, blue for saddle regions, cyan
for peaks, and magenta for pits
point which has the highest distance (altitude) to the line segment formed by the intersection
of a circle with a horizontal slice, which is designated as a potential nose tip. As the potential
nose tips are assumed to lie on the nose ridge, a line is fitted to them using the random sample
consensus algorithm (RANSAC). The potential nose tip, which lies on the consensus line and
has the highest altitude, is considered to be the final estimate of the tip of the nose.
2.4 3D Face Surface Feature Extraction and Matching
Feature extraction in 3D face recognition systems, as in the case of pattern recognition in
general, is a core stage that largely influences the performance and reliability of these systems.