Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
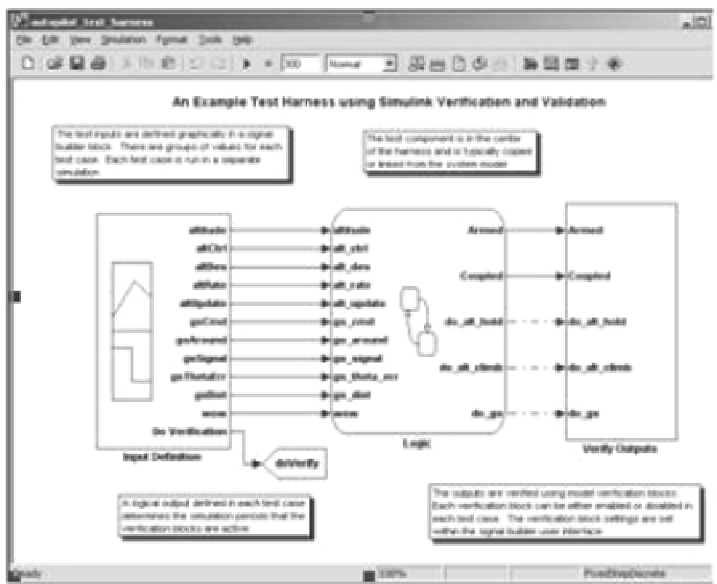
FIGURE 19.4
MATLAB/Simulink's verification and validation platform for logic test-
ing application extension; an example of a model-based development platform (Wakefield,
2008).
simulation of commonly engineered systems such as manufacturing, electrical, med-
ical, computational, mechanical, and communications. Commercial software simula-
tion tools are presently in a highly advanced state of development, having long since
proven their usefulness and reliability in many engineering fields in the global market-
place. An example of a model-based development platform is shown in Figure 19.4.
Figure 19.4 shows MATLAB/Simulink's Verification and Validation platform for
logic testing application extension (Wakefield, 2008).
Extensive efforts are made by simulation suppliers to upgrade continually and ex-
tend the application potential for their products. The concept of graphical modeling
is a simple representation of any physical system by its inputs—a “black box” con-
taining functional logic, and outputs. The approach can be a top-down or bottom-up
hierarchical structure within which each black box may contain multiple subsys-
tems, with the lowest level containing the basic logic and arithmetic operations. The
architecture of a given physical system is graphically arranged or designed graphi-
cally to simplify conceptualization and understanding of underlying logic. This has
tremendous advantages over the interpretation of a system by analysis of potentially
hundreds of thousands of lines of code.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search