Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
TABLE 15.1
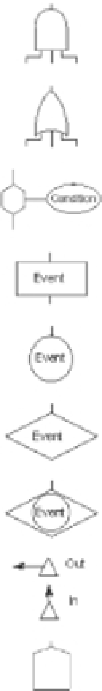
FTA Symbols
Symbol
Name
Meaning
And gate
Event above happens only if all events below happen.
Or gate
Event above happens if one or more of events below are met.
Event above happens if event below happens and conditions described in
oval happen.
Inhibit gate
Combination gate
Event that results from combination of events passing through gate below it.
Basic event
Event that does not have any contributory events.
Undeveloped
basic event
Event that does have contributory events, but which are not shown.
Remote basic
event
Event that does have contributory events, but are shown in another
diagram.
Transferred event
A link to another diagram or to another part of the same diagram.
Used to include or exclude other parts of the diagram that may or may not
apply in specific situations.
Switch
is developed by treating the component itself as a system made up of simpler refined
components (modules) whose failure probabilities can be measured by further testing.
These probabilities then are used in a model of the component of interest to produce
the required estimate (Knight & Nakano, 1997).
FTA of systems that include computers can treat the computer hardware much
like other components. Computer systems can fail, however, as a result of software
defects as well as hardware defects, and this raises the question about how the software
“components” of a system can be included in a fault-tree model. In practice, this has
proved difficult.
To obtain the probabilistic data needed for fault tree analysis, it is tempting to
analyze software in the same way that hardware is analyzed—either as a black-
box component whose failure probability can be measured by sampling the input








Search WWH ::

Custom Search