Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Risk
Analysis
Rapid
Prototype
Risk
Analysis
Rapid
Prototype
Risk
Analysis
Rapid
Prototype
Ta s k &
Schedule
Planning
Finished
Product
Te s t
Planning
System
Concept
System
Concept
Fine-Defect
recording
Coding
Standard
Software
Requirements
Postmortem
Requirements
Validation
Design
Design
Validation
Integrate
Design
Review
Detailed
Design
Te s t
Code
Code
Review
Compile
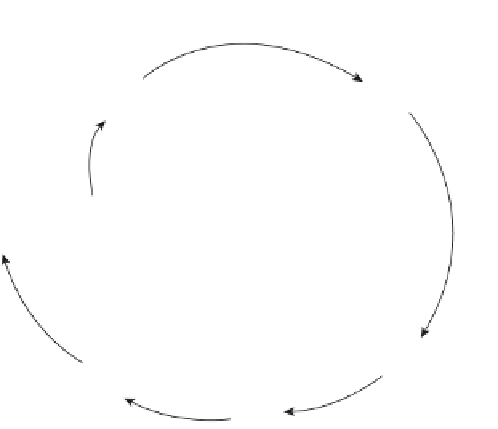
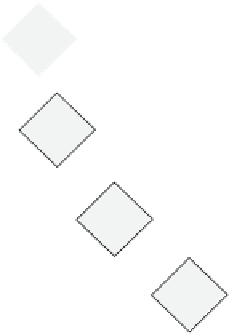
FIGURE 10.9
Practicing PSP & TSP using the Spiral Model.
team, transmission controls team, hybrid controls team, and OBDII compliance team
to discuss high-level requirements. The discussion included type of hybrid vehicle,
hybrid modes of the vehicle and power requirements, system requirements, hard-
ware and software interfaces between subsystems, subsystem boundaries/overlaps,
design guidelines, vehicle standards (SAE & ISO), communication protocols and
safety standards, application implementation and integration environment, and team
leaders/interfaces. Most requirements were finalized during the first few weeks and
agreed to between various teams. Once the high-level requirements were final-
ized, each of the requirements was discussed thoroughly with internal and external
interfaces.
Power-train vehicle architecture concepts were visited during this phase. As a part
of this discussion, it was determined that the typical internal combustion controls
tasks should be handled as is by the engine control unit, whereas a separate elec-
tronic control unit should carry out hybrid functionality with a core functionality to
determine the torque arbitration. It also was identified and determined that a separate
electronic control unit should be used to tackle alternative energy source controls.
Only the hardware and software interfaces for power-train controls and motor controls

















Search WWH ::

Custom Search