Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
y
0.4
N(0,1)
0.3
0.2
−
1.96
1.96
0.1
−
2.576
2.576
Encloses 95% of area under curve
99%
z
−
3
−
2
−
1
0
+
1
+
2
+
3
µ ±
1
σ
= 68.27%
µ ±
2
σ
= 95.45%
µ ±
3
σ
= 99.73%
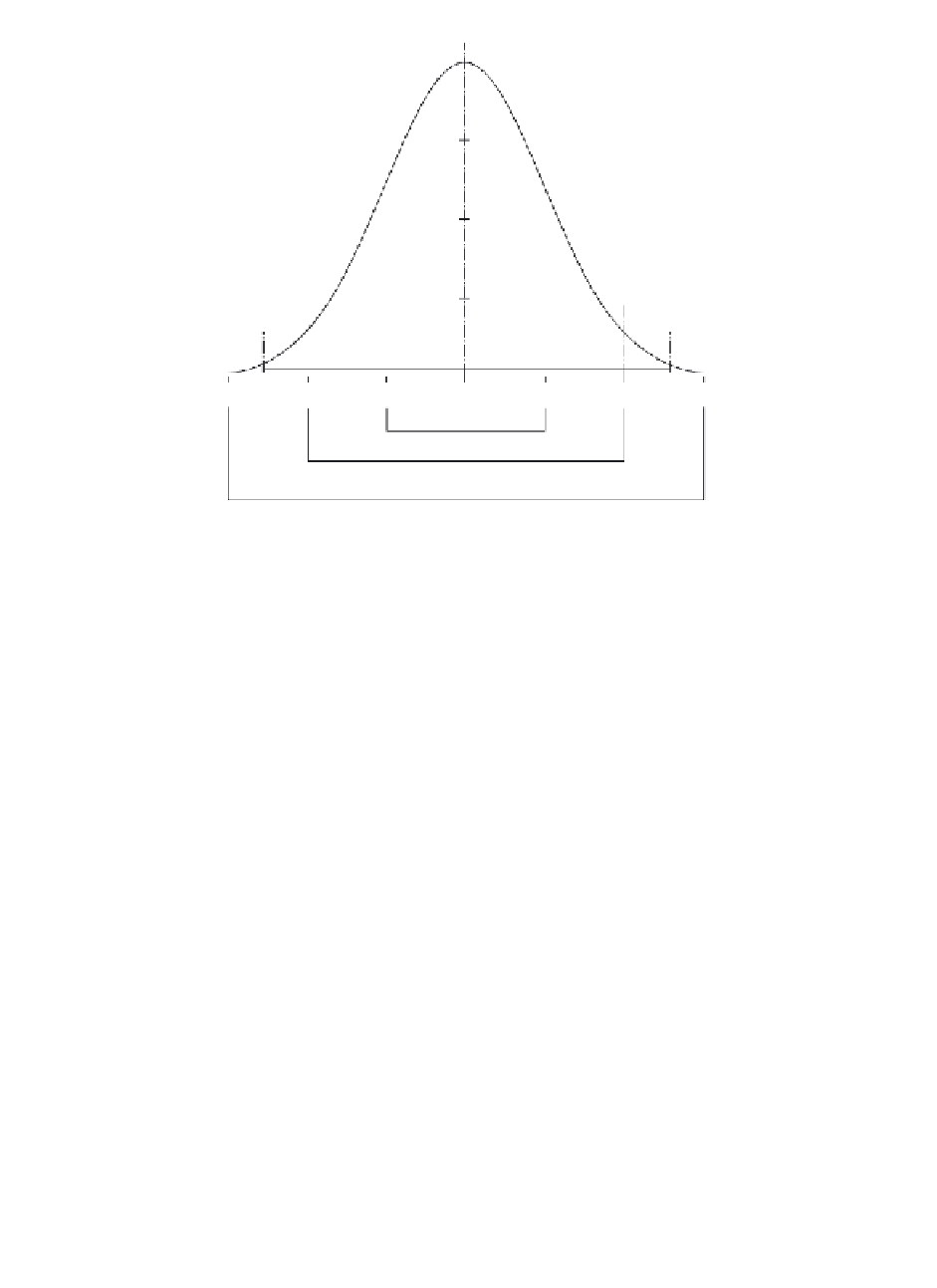
FIGURE 6.7
The standardized normal distribution
N
(0,1) and its properties.
0.0001, because in the normal distribution, almost all observations (i.e., more than
99.99%) fall within the range of
4 standard deviations. A population of measure-
ments with normal or Gaussian distribution will have 68.3% of the population within
±
±
(Figure 6.7).
The normal distribution is used extensively in statistical reasoning (induction),
the so-called inferential statistics. If the sample size is large enough, the results of
randomly selecting sample candidates and measuring a response or FR of interest
is “normally distributed,” and thus knowing the shape of the normal curve, we can
calculate precisely the probability of obtaining “by chance” FR outcomes representing
various levels of deviation from the hypothetical population mean of zero.
In hypothesis testing, if such a calculated probability is so low that it meets
the previously accepted criterion of statistical significance, then we only have one
choice: conclude that our result gives a better approximation of what is going on in
the population than the “null hypothesis.” Note that this entire reasoning is based
on the assumption that the shape of the distribution of those “data points” (technically,
the “sampling distribution”) is normal.
Are all test statistics normally distributed? Not all, but most of them are either
based on the normal distribution directly or on distributions that are related to, and can
be derived from, normal, such as Students
t
, Fishers
F
, or chi-square. Typically, those
tests require that the variables analyzed are normally distributed in the population;
that is, they meet the so-called “normality assumption.” Many observed variables
actually are normally distributed, which is another reason why the normal distribution
1
σ
, 95.4% within
±
2
σ
, 99.7% within
±
3
σ
, and 99.9% within
±
4
σ
Search WWH ::

Custom Search