Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
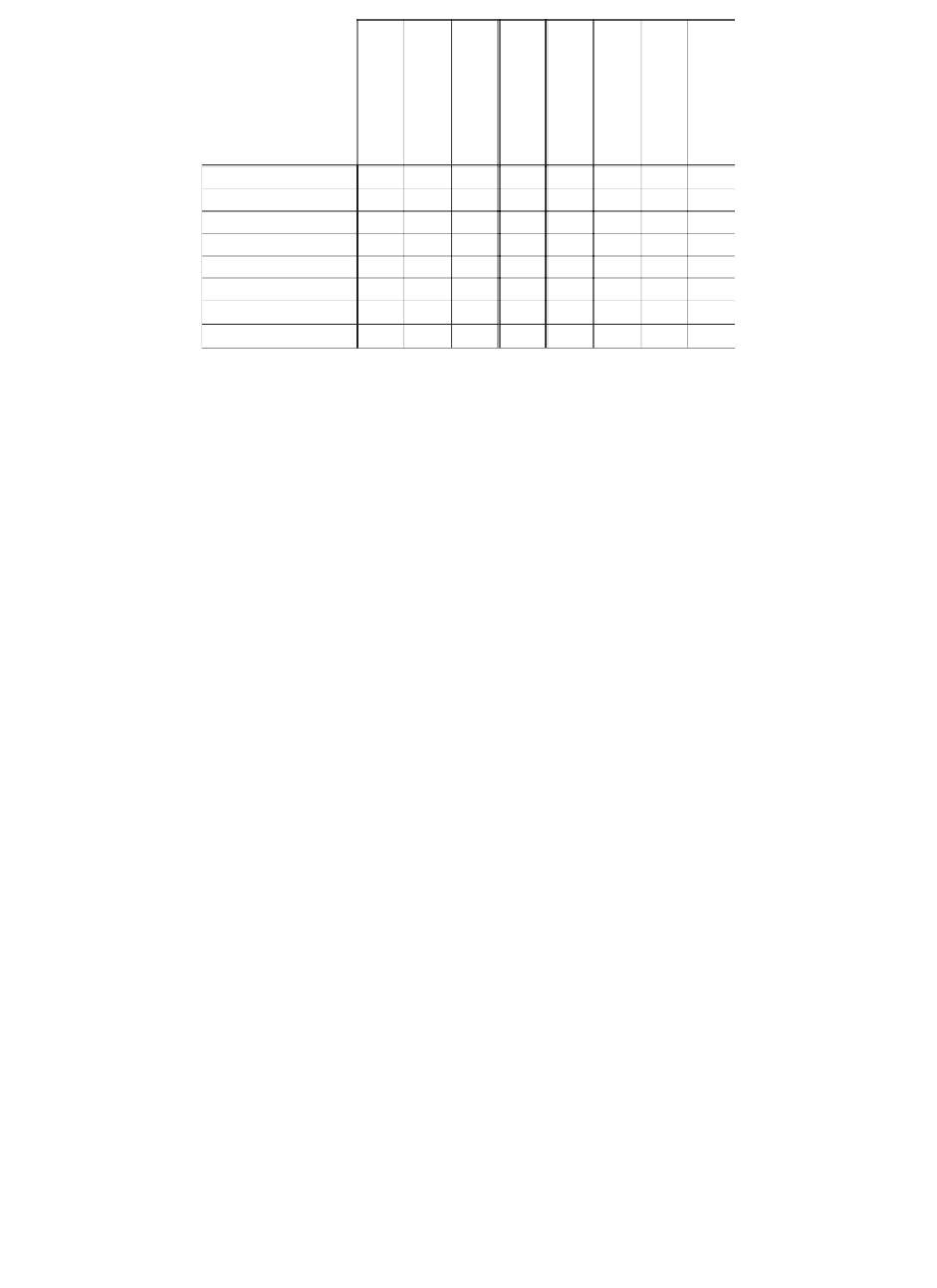
Capability
Usability
Performance
Reliability
Instability
Maintainability
Documentation
Availability
: Conflict One Another
: Support One Another
Blank: Not Related
FIGURE 5.3
IBM dimensions of quality.
6
In addition to Motorola, two leading firms that have placed a great deal of
importance on software quality as related to customer satisfaction are IBM and
Hewlett-Packard. IBM measures user satisfaction in eight attributes for quality
as well as overall user satisfaction: capability or functionality, usability, perfor-
mance, reliability, installability, maintainability, documentation, and availability (see
Figure 5.3).
Some of these attributes conflict with each other, and some support each other. For
example, usability and performance may conflict, as may reliability and capability
or performance and capability. Other computer and software vendor organizations
may use more or fewer quality parameters and may even weight them differently
for different kinds of software or for the same software in different vertical markets.
Some organizations focus on process quality rather than on product quality. Although
it is true that a flawed process is unlikely to produce a quality software product, our
focus in this section is entirely on software product quality, from customer needs
identification to architectural conception to verification. The developmental flaws are
tackled by a robust DFSS methodology, which is the subject of this topic.
5.6
SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT PROCESS METRICS
The measurement of software development productivity is needed to control software
costs, but it is discouragingly labor-intensive and expensive. Many facets of the
process metrics such as yield metrics are used. For example, the application of
6
http://www.developer.com/tech/article.php/10923 3644656 1/Software-Quality-Metrics.htm









Search WWH ::

Custom Search