Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
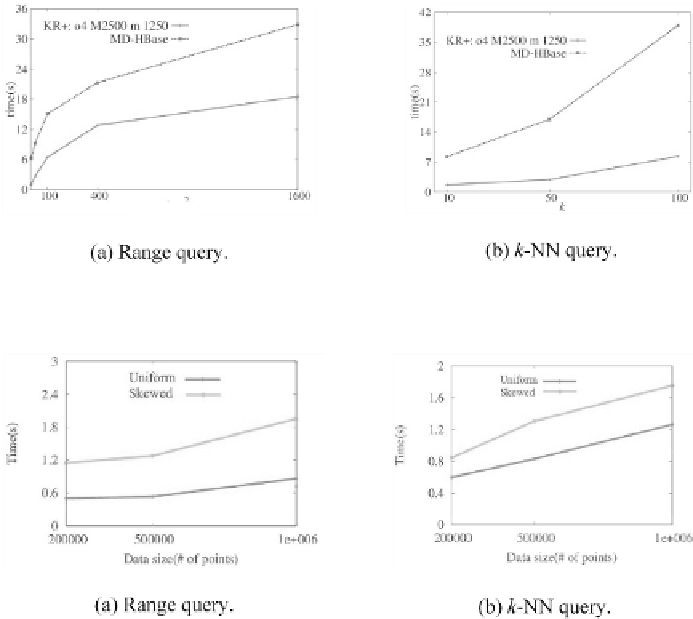
10 is about 1.7s. However, MD-HBase for range query 1 km × 1 km is about
6.2s and
k
-NN query when k = 10 is about 8.2s. The result of the evaluation
shows that our KR
+
has much better performance for range query and
k
-NN
query. Besides, KR
+
overcomes the trade-off between the number of points
for getting one key and the number of keys for scanning so that it is more
effi cient than MD-HBase, especially for skewed data.
In addition, we study the scalability of the proposed index method
by varying the data size (i.e., the number of points) in Fig. 10. In the
experiments, we set the parameters as M = 250, m = 125, o = 8, and k =
1000. As shown in the experiments, the response time of the range query
(or
k
-NN query) slightly increases as the data size is increased from 200,000
to 1,000,000. The response time increases as the data size increases because
more points would need to be fetched.
36
42
KR+: o4 M2500 m 1250
MD-HBase
30
KR+: o4 M2500 m 1250
MD-HBase
35
24
28
18
21
12
14
6
7
0
0
100
400
1600
10
50
100
k
range(km
2
)
(a) Range query.
(b)
k
-NN query.
Fig. 9.
Skewed data distribution.
Color image of this figure appears in the color plate section at the end of the topic.
3
2
Uniform
Skewed
Uniform
Skewed
2.4
1.6
1.8
1.2
1.2
0.8
0.6
0.4
0
0
200000
500000
1e+006
200000
500000
1e+006
Data size(# of points)
Data size(# of points)
(a) Range query.
(b)
k
-NN query.
Fig. 10.
Effect of data size.
Color image of this figure appears in the color plate section at the end of the topic.



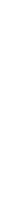












Search WWH ::

Custom Search