Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
is independent from features, its correlation remains invariant by varying
occurrences of attributes.
In Table 7 and in Fig. 11, the correlations of the above mentioned
methods with human judgment by changing the occurrences of parts are
shown. We observe that the values obtained by the
GSim
method are higher
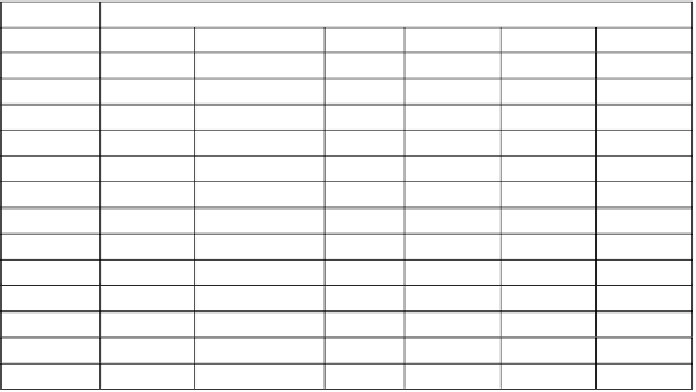
Table 7.
Results about similarity methods by changing occurrences of parts.
Correlation
Parts
Lin
Dice
MDSM
v
MDSM
c
GSim
v
GSim
c
7
0.7127
0.2972
0.3552
0.4007
0.7928
0.6056
9
0.7127
0.2972
0.3585
0.3912
0.7839
0.6652
11
0.7127
0.2972
0.3621
0.3799
0.7737
0.7137
13
0.7127
0.2972
0.3659
0.3692
0.7621
0.7517
15
0.7127
0.2972
0.3697
0.3593
0.7499
0.7816
17
0.7127
0.2972
0.3737
0.3507
0.7364
0.8037
19
0.7127
0.2972
0.3774
0.3419
0.7214
0.8198
21
0.7127
0.2972
0.3821
0.3368
0.7050
0.8312
23
0.7127
0.2972
0.3864
0.3309
0.6873
0.8392
25
0.7127
0.2972
0.3908
0.3260
0.6672
0.8440
27
0.7127
0.2972
0.3948
0.3216
0.6460
0.8469
29
0.7127
0.2972
0.3984
0.3176
0.6237
0.8482
31
0.7127
0.2972
0.4014
0.3142
0.5996
0.8483
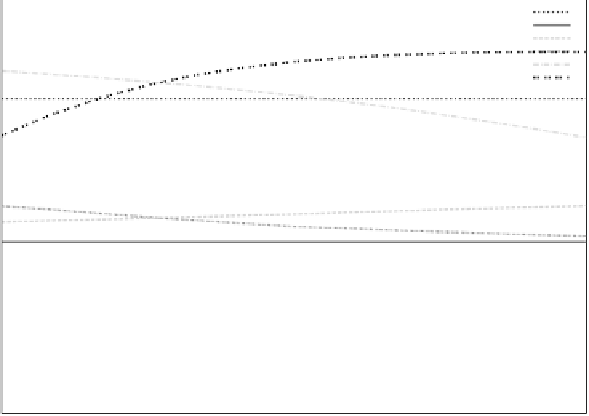
1
Lin
Dice
MDSM
v
MDSM
c
GSim
v
GSim
c
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
-0.2
7
11
15
19
23
27
31
Attributes
Fig. 11.
Correlation of methods by varying occurrence of parts.
Color image of this figure appears in the color plate section at the end of the topic.













Search WWH ::

Custom Search