Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
uniform probabilistic weighted arc
. Accordingly, in formula (2), the weight of
arc is
w
a
(
i
-1,
i
)
= (
1
(
k
-1)
)
(
i
-1)
, and weights are denoted by
w
pa
.
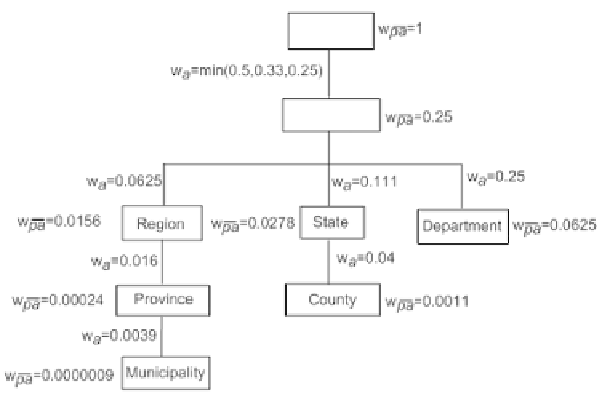
For instance, in Fig. 5, consider Path3: <
Top, Country, Region, Province,
Municipality
>. In this case,
k
=5. The weight of arc connecting
Region
(node
3) and
Province
(node 4) (i.e.,
w
a(Region,Province)
= w
a
(3,4)
=(
1
(5-1)
)
(4-1)
) is equal to (
1
/
4
)
3
= 0.016. Similarly, the weights of remaining concepts are computed.
In this approach, with respect to the previous uniform probabilistic
weighted arc approach, the weights associated with arcs along a path are
different and the weight decreases as the length of a path increases.
w
pa
=1
To p
w
a
=min(0.5,0.33,0.25)
Country
w
pa
=0.25
w
a
=0.25
w
a
=0.0625
w
a
=0.111
w
pa
=0.0156
Region
w
pa
=0.0278
State
Department
w
pa
=0.0625
w
a
=0.04
w
a
=0.016
Province
w
pa
=0.00024
County
w
pa
=0.0011
w
a
=0.0039
Municipality
w
pa
=0.0000009
Fig. 5.
Hierarchy weighted by non-uniform probabilistic weighted arc approach.
Similarity methods
We focus on three types of similarity methods, namely information content-
based, feature based and combined approaches.
Information content-based method
As anticipated, the information based approach to measuring semantic
similarity is based on the proposal of Resnik (1995), which has been
successively refi ned by Lin (1998). Resnik views noun synsets as a class
of words, where the class is made up of all words in a synset as well as,
directly or indirectly, words in all subordinate synsets. Thus, conceptual
similarity is considered in terms of class similarity.
According to the Resnik's approach, the similarity between two
hierarchically organized classes (or concepts),
Sim
R
, is given by the




















Search WWH ::

Custom Search