Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
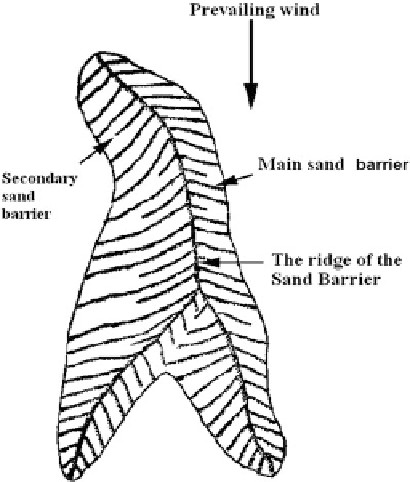
Fig. 2.14
The disposing
patterns of sand barrier on the
complicated irregular sand
dune
smaller in those areas where the wind is strong, and on the top of the dunes. In other
areas, the spacing can be increased. In general, the row spacing of sand barriers
can be determined on the basis of the following factors: (1) The
height of the sand
barrier
: the higher the sand barrier, the wider the row spacing; (2) The
slope of sand
surface
: the steeper the slope, the closer the row spacing; (3) The
wind force
:the
stronger the wind force, the closer the row spacing; (4) The
part of sand dunes
:
the row spacing is closer on the top than that at the foot of the sand dunes; (5) The
structure of the sand barrier
: the denser the structure of the sand barrier, the closer
the row spacing.
High Standing Sand Barrier
Under normal conditions, on a gentle slope, which is less then 4
ı
, the row spacing
of sand barriers should be 10-15 times the height of the sand barrier. Of course, the
wind force should be considered in this case. When the sand barriers are set up on
the windward slope, the base of the barrier which is located on the upper part of the
dunes should be lower than the tip of the next barrier which is situated to the lower
part of sand dunes (see Fig.
2.15
).
When barriers of a given height are set up on the slope of sand dunes, the row
spacing is closer for the steep slope and wider for the gentle slope. The steeper slope
of the sand dunes, the closer the row spacing of the barrier (Fig.
2.16
).
There is a close relationship between row spacing of sand barriers and the height
of sand barriers, as well as the slop of sand dunes (see Table
2.1
).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search