Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
TOMS Anomalies
TOMS Std Dev
0.4
0.2
0.0
-0.2
-0.4
1996
1997
1998
1999
2000
2001
Years
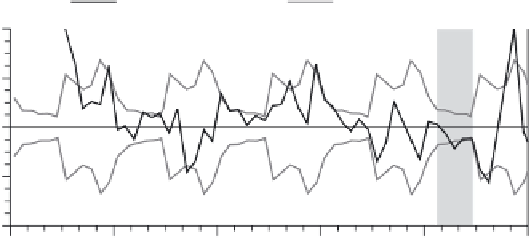
Figure 20.4
The relationship between flood inundation of Etosha Pan, Namibia, and subsequent dust events. Data show inunda-
tion of the pan due to heavy rains in 1997 and 2000 with associated lows in TOMS AI anomalies (monthly mean values minus mean
of all monthly means), suggesting limited dust activity during and immediately after the flood events. However, in 1998-1999
and late 2000 there are anomalously high values in TOMS AI anomalies (larger than 1 standard deviation), possibly as a result
of the replenishment of the pan with erodible material. Fluctuations in measured wind speed do not explain these dust patterns
(after Mahowald
et al.
, 2003).
Nickling, 1999), investigations by Mahowald
et al.
(2003)
and Bryant
et al.
(2007) have noted that the dry lake beds
that constitute the most important dust source regions in
southern Africa (Etosha Pan in Namibia and the Mak-
gadikgadi Pans in Botswana) are reliant on intermittent
flood inundation to provide erodible sediment for aeolian
erosion in the following years (Figure 20.4). They found
that a large proportion of the variability in dust emission
from these sources could therefore be linked to changing
rainfall patterns driven by the El Ni no-Southern Oscil-
lation (ENSO). Similar positive and lagged relationships
between rainfall and dust emission have also been noted
in north America (Reheis, 2006).
Human activity can have a profound influence on gen-
erating new dust sources (see Chapter 23 for a full dis-
cussion). Key human impacts that accelerate wind erosion
and cause significant dust emission involve the break-up
of stable dryland surfaces by both off-road vehicle (ORV)
activity (Goossens and Buck, 2009) and agricultural ac-
tivity on susceptible soils, as occurred during the Dust
Bowl in the mid-west USA in the 1930s (Worster, 1979).
Particularly significant dust sources initiated by human
activity also derive from the exposure and desiccation of
sediment after the draining of inland water bodies such
as Owens Lake in the USA (Gill, 1996) and the Aral Sea
(O'Hara
et al.
, 2000).
and on the size, shape and mass of the particles them-
selves. Larger particles tend to have higher deposition
velocities and so are deposited closer to source than fine
particles (Tsoar and Pye, 1987; Pye, 1995). Thus 'dry'
deposition can be a very efficient sorter of particles. In
this way, Saharan dust transported across the Atlantic
is seen to be much finer at distance from source, with
median deposited particle sizes in Morocco measured at
22.0-37.0 µm (Khiri, Ezaidi and Kabbachi, 2004) and
those deposited in the Caribbean at 4.0 µm (Petit
et al.
,
2005). In contrast 'wet' deposition, where particles are
drawn out of the airflow by rain, cleanses the atmosphere
and results in a much less sorted deposit (Figure 20.5).
At regional scales such a fining in deposited particles
with distance from source is much more difficult to as-
certain because such deposits often derive from multiple
dust sources (Cattle, McTainsh and Elias, 2009) and so
'fingerprinting' of sources from deposits using grain size
analysis can be complicated (Wiggs
et al.
, 2003).
Rates of dust deposition can be very high close to source
areas with a steep decay in deposition rates with increas-
ing distance from source (Figure 20.6). In a 3 month study
Wiggs and Holmes (2010) reported average deposition
rates of 48 g/m
2
(with a maximum of nearly 30 g/m
2
in a period of 2 weeks) immediately downwind of an
eroding agricultural field in South Africa, while O'Hara,
Clarke and Elatrash (2006) measured rates of 276 t/km
2
yr
in Libya. In Australia, rates between 31 and 44 t/km
2
yr
have been measured by McTainsh and Lynch (1996) while
maximum rates equivalent to 102 t/km
2
20.1.1.3
Dust sinks
Once entrained, dust-sized particles will be transported in
the atmosphere with deposition dependent upon changing
yr have been re-
ported by Cattle, McTainsh and Elias (2009). However,