Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
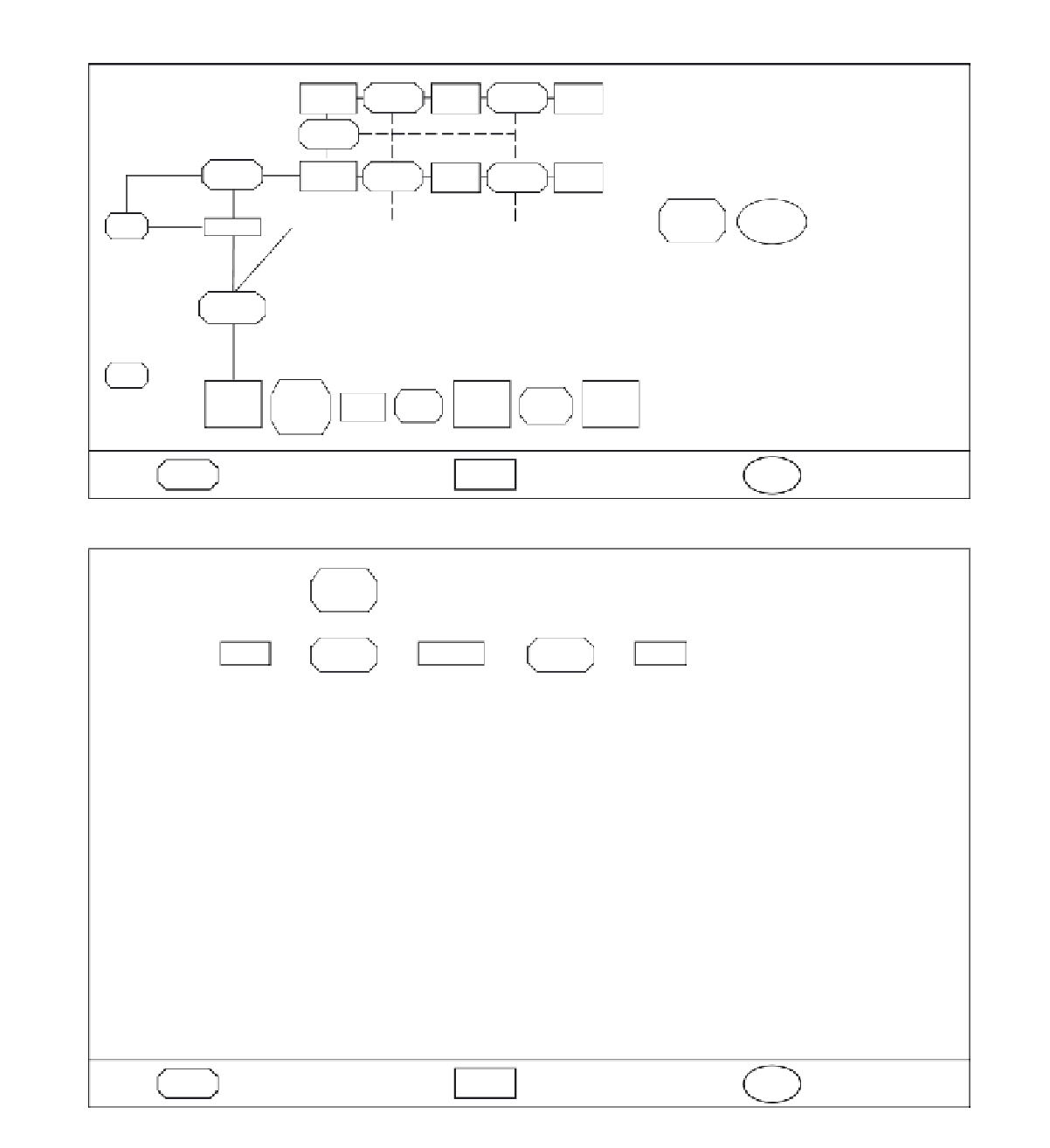
(a) soil-covered slope-erosion system
Mixing,
weathering
Soil
Saprolite
Weathering
Bedrock
RIDGE
Creep,
weathering
Creep,
weathering
Mixing,
weathering
Soil
Saprolite
Weathering
Bedrock
SIDE SLOPE
Dissolved
load
transport
Dissolved
load
discharge
Splash,
wash
Hollow
Suspended
load
transport
Suspended
load
discharge
Translational
slide or flow
Bed
material
attrition
Rill and
gully
Debris
torrent,
high
stream
discharge
Sediment
in
tributary
channels
Sediment
on main
valley
floor
Active
sediment
in main
channel
Debris
fan
erosion
Bed and
bank
erosion
Debris
fan
Bedload
transport
Bedload
discharge
Transfer processes
Storage systems
Outputs
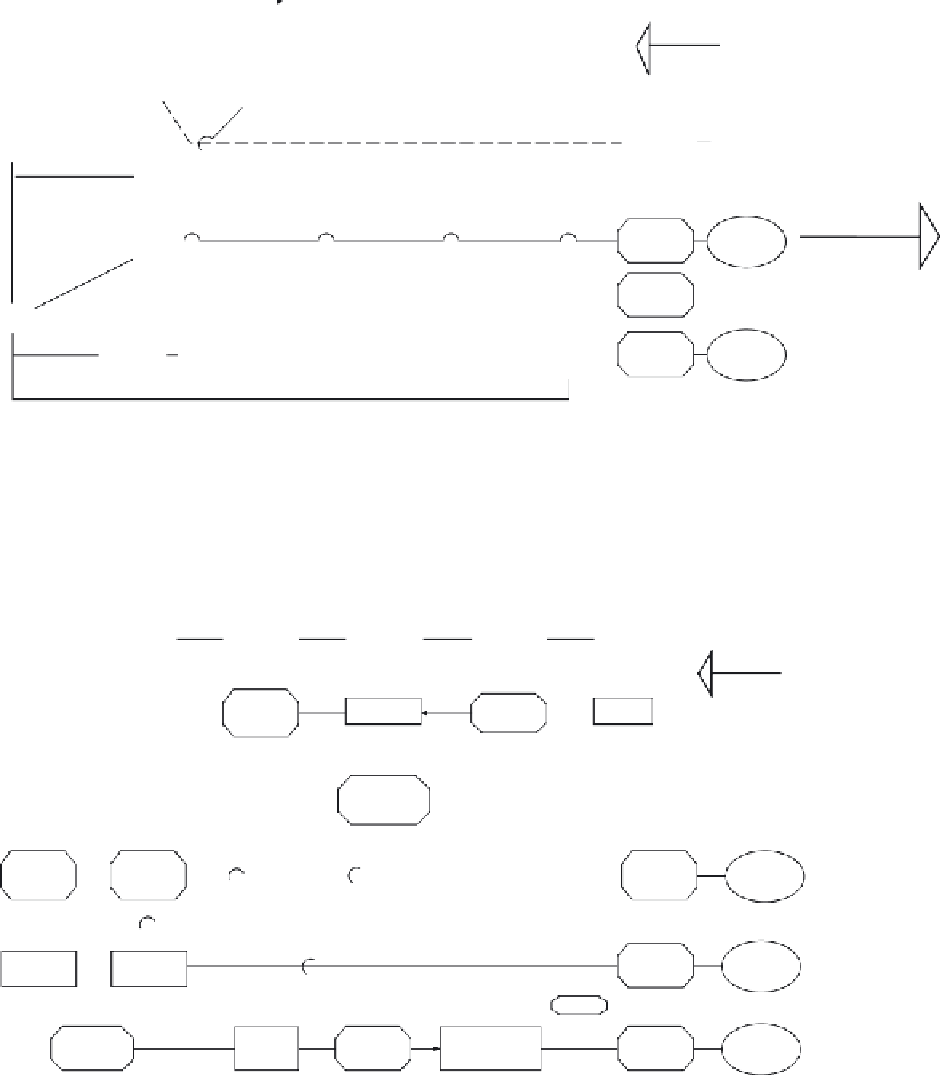
(b) rock-slope-erosion system
Snow
and ice
avalanches
Creep,
rock fall
Physical
weathering
Talus
Felsenmeer
Bedrock
Block falls,
topping
failures
Joint
opening
Cliff faces
Bedrock
Slumps, rock
slides and
avalanches
Chemical
weathering,
creep
Dissolved
load
transport
Dissolved
load
discharge
Debris flow,
wash, stream
Suspended
load
transport
Suspended
load
discharge
Debris cone,
alluvial fan
Soil
Attrition
Sediment
in
channels
Active sediment
in bed, braid and
point bars
Toe erosion,
rill and gully
erosion
Bed and
bank
erosion
Bedload
transport
Bedload
discharge
Transfer processes
Storage systems
Outputs
Figure 10.2
A process-based approach to understanding slope systems: the store and transfer model of Dietrich and Dunne
(1978) as modified by Selby (1993). The slope-erosion system for (a) soil-covered landscapes and (b) rock slopes.