Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Somatic cells
CycD-CDK4/6
CycE-CDK2
CycA-CDK1/2
CycB-CDK1/2
CDT1
CDC6
Replication
licensing
G1
S
G2
M
G1
Geminin
APC/C activity
CyclinA
CyclinB
Geminin
CDT1
EMI1
ESCs
CycA
**
-CDK1/2
CycB
**
-CDK1/2
CycE-CDK2
CDT1
**
CDC6
G1
S
G2
M
G1
G1
S
G2
M
Geminin
APC
/C ac
tivity
CDT1
EMI1
**
EMI1
**
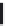
Figure 7.2 Cell-cycle regulators in somatic cells and ESCs. Differences in the activity
of key cell-cycle regulators in somatic and ESCs are shown. In ESCs, CDK activity is
high throughout cell cycle and only minimal oscillation is detected (
Ballabeni et al.,
2011
). CycD-associated CDK activity is not detected in ESCs. APC/C activity is atten-
uated presumably due to abundant EMI1, an inhibitor of APC/C. Geminin prevents
extra rounds of DNA synthesis by binding and inhibiting the replication licensing
factor CDT1. This interaction is promoted by CDK activity (
Ballabeni et al., 2004
),
which helps protect CDT1 from degrading by APC/C. When geminin is degraded
by APC/C during G1, CDT1 is released from geminin to promote replication. Abundant
functional CDT1 during G1 may allow ESCs to transition from G1 to S, despite atten-
uated APC/C function. **Indicates abundant proteins in ESCs due to attenuated
APC/C activity.