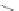Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 6.13
Two Basically
Different Cases for the
Vertex b
(1,1)
x
1,3
Base
(1,1)
x
2,2
a
Base
b
For computing distance matrix of this nanotube we must compute matrices
D
(a
m
×
n
=
[d
i,j
] and D
(b)
[d
i,j
]. By these calculations, on can see that
=
m
×
n
⎧
⎨
⎧
⎨
Max
{
a
i,j
,b
i,j
}
1
≤
j
≤
n
/
2
Max
{
a
i,j
,c
i,j
}
1
≤
j
≤
n/2
d
i,j
=
and d
i,j
=
.
⎩
⎩
d
i,n
−
j
+
2
j
>
n
/
2
+
1
d
i,n
−
j
+
2
j
>
n/2
+
1
By continuing this method, the mentioned authors proved that:
Theorem 5
Suppose A and B are an armchair and zig-zag polyhex nanotube, re-
spectively, with exactly m rows and n columns, Fig.
6.2
. Moreover, we assume that
C is a polyhex nanotorus with similar parameters. Then,
1. (Yousefi and Ashrafi
2007
)
⎨
⎩
n
2
[1
m
2
n
12
n
8
(
n
2
+
(3n
2
m
2
1)
n
]
+
−
4)
+
−
1)
−
(
−
m
≤
1
⎡
⎣
(
⎤
⎦
W(A)
=
,
n
2
mn
2
24
n
3
192
(n
2
n
8
m
>
n
(n
2
+
4m
2
+
3mn
−
8)
−
−
16)
+
−
1)
−
1
2
+
1
2. (Ashrafi and Yousefi
2007a
)
⎧
⎨
mn
2
24
m
2
n
12
n
2
+
(4m
2
(m
2
+
3mn
−
4)
+
−
1)
m
≤
1
W(B)
=
.
⎩
mn
2
24
n
3
192
(n
2
m
>
n
(8m
2
n
2
+
−
6)
−
−
4)
2
+
1