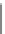Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 5.2
Cartoon depicting
SiC nanowires growth with a
particular focus on the
dewetting stage: (
a
) and (
b
)a
uniform film of metal catalyst
(
in red
) is deposited on the
substrate (
in blue
), (
c
) after
the eutectic temperature is
reached and the catalyst is in
liquid phase, the film forms
liquid droplets all over
substrate surface. (
d
) An axial
growth takes place nucleated
by the catalyst particles,
which remain on the top of
the wires
In semiconductor technology nickel silicides are finding increasing interest,
therefore nickel diffusion in silicon is widely studied and it is possible to find
many examples in literature of studies on nickel diffusion of Ni in silicon. The
nickel diffusion through the bulk is faster than that on nickel diffusion in silicon
surface and the transport to the surface is caused by the segregation when the
solubility of nickel reduces owing to the temperature decrease. The shape and
the state of the structures on surface is dependent on the cooling rate (Dolbak
et al.
1989
,
1991
). The observation of square-shaped island is typical for the
segregation of nickel on (100) surface of silicon.
The dewetting of a 2 nm thick Au layer performed at 600
◦
C is shown in Fig.
5.4
: the
size of the islands here is much smaller because the eutectic temperature of silicon-
gold system is lower (363
◦
C (Okamoto and Massalski
1983
) and the cohesion forces
are less.
Table 5.1
Comparison between the alloy eutectic temperature reported in literature and the
temperature set to obtain the dewetting of the samples
Metal Catalyst
Alloy eutectic temperature
◦
C
Dewetting temperature
◦
C
Ni
966 (Nash and Nash
1987
)
1100
Fe
1200 (Massot et al.
2013
)
1250
Au
363 (Okamoto and Massalski
1983
)
600