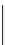Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
V
b
I
b
T
I
dchg
Data
logger
+
V
batt
I
chg
SOC
calculation
I
dchg
R
int
V
batt
C
dbl
C
bulk
Time (s)
Figure 10.43 Battery characterization test stand
voltage,
V
batt
, consists of a step change proportional to the battery internal resis-
tance times the discharge current magnitude. Immediately following the voltage
step is a relatively steep capacitive time constant discharge representing the bleed
off of double layer capacitance of the battery. For longer discharge times, for
example greater than 10 s, the bulk storage electrochemical time constants are
entered and the voltage during discharge is more stable with only a slight negative
slope. For a typical automotive battery, the model that can be obtained from such
characterization testing is given in Figure 10.44.
V
pol
R
int
V
oc
+
R
leak
I
V
o
C
dbl
C
bulk
SOC
Figure 10.44 Pb-acid battery empirical model
Model parameters for a typical, 70 Ah automotive SLI battery are
R
int
¼
7m
W
,
C
dbl
¼
110 F and
C
bulk
¼
10
6
F, with an initial condition of the battery open circuit
voltage minus the polarization charge of approximately 0.8 V. A resistor,
R
leak
, was
added to the empirical model to account for self-discharge of typically 2.5%/month
of stand time.
More refined battery models consist of conductance measurements in which a
low voltage ac signal is impressed across the battery terminals, and the resulting
current into the battery terminals is measured. Voltage, current, temperature and
time are logged during the characterization, and from these data battery con-
ductance, immittance and frequency response are computed. Battery conductance