Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
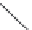
Current collector
Electrode
Carbon matrix
d
2
C
eq
Electrolyte (ACN + TEATFB)
C
eq
Separator
Electrolyte (ACN + TEATFB)
2
C
eq
Carbon matrix
Electrode
Current collector
Figure 10.18 Ultra-capacitor cell construction
metallic cell package, plastic covering, end seal and terminations. AN is a toxic sub-
stance on its own, but in the ultra-capacitor it is in solution with other organic con-
stituents and in low free volume since it is mostly absorbed into the AC electrodes and
separator. There is generally no safety concern with AN even if the ultra-capacitor is in
overvoltage and outgassing of the electrolyte occurs. However, should the gas effluent
be burned in an oxygen starved atmosphere then there is the potential to generate
cyanide gas, HCN. Application of ultra-capacitors into vehicles must take into account
proper installation, crash worthiness and abuse, just as lithium ion and advanced bat-
tery systems. Today, there are numerous toxicology tests being performed by various
testing institutions that validate claims of its safe use.
The ultra-capacitor gets its enormous surface area from the porous carbon
based electrodes that can provide nearly 2,000 m
2
/g. The charge separation distance
is not dependent on any dielectric paper or film or ceramic, but by the size of the
ions in the organic electrolyte that is on the order of angstroms. Figure 10.19 is an
illustration of ultra-capacitor carbon electrode porosity and ion size, including an
illustration of how charged ions accumulate into the various regions of activated
carbon electrode pores. Pores on the nanoscale can have a diameter on the order of
the ions, so that accumulation of ions into these pores is blocked. If this is the case,
the EDLC effect is not seen for either aqueous or organic electrolytes.
Ion diameter
~1 nm
Nano pore
<1 nm
diameter
Nano pore
<1 nm diameter
-
Electrolyte
ion
+
Electrolyte
solution
-
+
-
Micro pore
>1.5 nm
diameter
Micro pore
>1.5 nm
diameter
Electrolyte solution
-
-
-
+
-
+
+
+V
Activated carbon
electrode deposit
Activated carbon
electrode deposit
-
+
-
-
+
+
+
+
+
Meso and macro
pores
Meso and macro pores
Figure 10.19 Illustration of an electronic double layer capacitor system