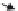Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Power electronics
V+
Curr.
sense
U
V
W
Phase output
U
V
W
V
f
,
I
f
Phase leg
currents
H
-U
H
-V
H
-W
L
-U
L
-V
L
-W
I-trip
Controller
uC
or DSP
Monolythic driver
IPEM
C'md's
Figure 6.1 IPEM schematic
In Figure 6.1, motor current is monitored by individual phase leg current sense
resistors to implement ground fault protection. A single current sense resistor can
also be used. For improved temperature stability a manganin shunt can be used in
place of carbon or wire filament wound sense resistors. A microcontroller or DSP
interprets user input commands and generates high and low side gate signals to the
IPEM according to the desired PWM algorithm. An overcurrent trip signal is used
to override input logic commands in the event of motor stall or fault. Gate driver
logic power for the upper switches in a phase leg is provided by bootstrap capa-
citors connected from the phase output to the IPEM gate circuit.
There is now a concentrated effort to fully integrate motor drive systems, as
depicted in Figure 6.1, into a chip. The goal of power electronics remains the reali-
zation of a fully digital motion control system that is fully integrated for high reliability
and compact packaging. Subsections 6.2 through 6.4 explore the various types of
motion control PWM algorithms used to synthesize the motor voltages and currents.
The most fundamental modulation technique, six step square wave, has been
discussed in the previous chapter in relation to brushless dc machine control. This
technique, also referred to as block modulation, presents the most basic electronic
current commutation method.
6.1 Semiconductor device technologies
Power electronics is still relatively immature technology even as silicon based signal
level and power level devices have grown into huge markets. But at power levels of