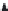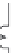Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
C
A
Phases:
A
B
B
C
A
B
C
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
1
21
5
25
9
29
13
33
17
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
56
40
60
44
64
48
68
52
72
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
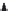
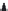
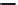
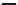
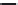
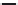
Figure 5.46 12-pole inverter connections and control. The elementary coils are
connected in series, as shown in Figure 5.45. All nine inverter totem
poles are used
A
B
Phases:
A-A
-B
B
C
-C
C
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
1
21
5
25
9
29
13
33
17
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
56
40
60
44
64
48
68
52
72
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
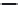
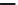
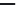
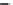
Figure 5.47 4-pole inverter connections and control. The elementary coils are
connected in series, as shown in Figure 5.42. All nine inverter totem
poles are used
The conventional winding connections for (1:odd number) and (1:even num-
ber) combinations will be illustrated by two examples.
Speed ratio (1:odd number) - full pitch winding at lower polarity.
Consider an
AC winding that has to operate in 4-pole and in 20-pole connection. For PPM
implementation, the winding will be double layered and will have 5 phases at 4
poles (
m
4
¼
5) and 2 phases at 20 poles (
m
20
¼
2). Phase belt at 4 poles is
q
4
¼
2,
and at 20 poles
q
20
¼
1. Coil pitch is expressed as the number of teeth,
y
¼ t
p
,4
¼
10, and the winding is placed in 40 slots.
●
Winding configuration at two polarities is shown in Figure 5.45. For purpose
of clarity, only coils belonging to 1-phase, that is, carrying the same current, are
shown in this figure. Current direction in the coils is given by the arrows.
For the 4-pole connection illustrated schematically in Figure 5.48 (top), the
adjacent two coils belong to the same phase (
q
4
¼
2). The pole areas are denoted by
N
4
and
S
4
.