Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
400
350
Peak torque (380 Nm)
300
Intermittent output
250
200
Continuous output
150
100
50
65
0
0
500
1,000
1,500
2,000 2,500
Speed (rpm)
3,000
3,500
4,000
4,500
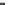
Figure 4.15 M/G torque-speed capability envelope (unique-mobility
HighTor motor)
It is instructive to walk through the operational regions of Figure 4.15 so that
no misunderstanding exists regarding what the M/G is capable of. The horizontal
line labelled peak torque is up to 250% of continuous operating torque and repre-
sents a sizing specification carried over from industrial induction motors. Industrial
motors have continuous ratings that reflect their thermal limitations of typically
40-60
C temperature rise over ambient necessary to protect their insulation sys-
tems from cumulative degradation and eventual failure. In the past this meant that
the industrial induction motor was capable of momentary (10-30 s) overdrive
conditions without incurring thermal excursions beyond 180
C at stator hot spots.
In automotive applications, particularly hybrid propulsion, the M/G rating
retains this industrial rating nomenclature for continuous and peak intermittent
operation. But there are mitigating factors. Although the industrial motor generally
does not have an electronic interface, it could be overloaded to its breakdown
torque, typically 250% of the thermal limited torque in class B designs, for short
durations. The region bounded by the speed axis, the torque axis, the flat line
representing constant torque, and a vertical to trapezoidal boundary back to the
speed axis represents the constant torque operating region. In the constant torque
operating region, the power electronic inverter has sufficient voltage from the dc
bus (battery or ultra-capacitor or generator or some combination) to synthesize
currents for injection into the electric machine. When the machine speed increases
to the corner point speed defining the break point between constant torque and
constant power, the inverter has essentially run out of voltage, the modulator
that regulates current synthesis begins pulse dropping and the process ends with the
inverter entering six step mode (also called block mode). Constant power is
the region of field weakening bounded by the already mentioned constant torque
region plus the hyperbola that defines the continuous or intermittent power