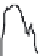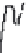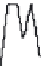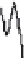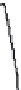Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
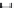
(a)
Length
=
598 s, distance
=
1.18 mi, average speed
=
7.1 mph
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
Test time (s)
(b)
Length = 892 s, distance = 3.94 mi, average speed = 15.97 mph
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
Test time (s)
Figure 3.14 Other drive cycles for consideration: (a) New York City cycle
driving schedule; (b) Japan 10-15 emission and fuel economy
driving schedule
3.4.3 Average speed and impact on fuel economy
The fact that standard drive cycles have considerable variation in their average and
maximum speeds means that fuel economy and performance attributes for each
cycle will have a different impact on driveline design. For example, Figure 3.15
illustrates how fuel economy varies by drive cycle as the transmission used to
match the engine to the driven wheels has its gear shift ratio coverage varied. For
each geographical area there is a transmission design, summarized by its gear shift
ratio coverage, that best matches the vehicle to the standard drive cycle.
Notice the distinct one-to-one match-up between the peaks of fuel economy
versus transmission gear shift ratio coverage in Figure 3.15 when compared to
Table 3.5 data for maximum vehicle speed by drive cycle (first three rows).