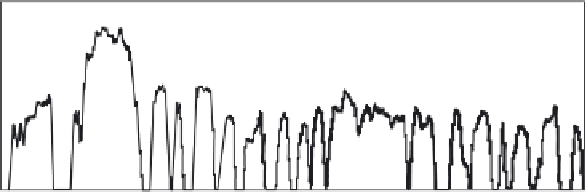Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
modulates the out-board wheels, slowing them down, so that oscillatory motion is
avoided.
Regardless of whether the vehicle is a low cg passenger vehicle, or a higher cg
SUV, the stability programme reacts far faster than a human operator and corrects
the yaw motion. With the system disabled, each lane change manoeuvre at the same
speed resulted in a complete loss of vehicle control and some very aggressive side
skids.
3.4 Drive cycle implications
The US Federal Urban Drive (FUD) cycle was created during the early years of
battery electric vehicle (BEV) development to model urban driving conditions
(Figure 3.10).
700
600
500
400
300
200
100
0
Time (s)
Figure 3.10 FUD standard drive cycle used for BEV development (wheel speed)
The FUD cycle is the first 1,369 s of the Federal Test Procedure FTP75. FUD
cycle represents an urban drive of 7.45mi at an average speed of 19.59 mph.
3.4.1 Types of drive cycles
A great number of drive cycles have been developed to mock-up the driving habits
of large populations of drivers in particular geographical areas. The main drive
cycles of interest to hybrid propulsion designers are the Environmental Protection
Agency (EPA), city and highway cycles used in North America. In Europe the New
European Drive Cycle (NEDC) is used extensively. In Asia-Pacific, and particu-
larly Japan, the 10-15 mode is used almost always. There are other related, but
revised for some particular attribute, drive cycles, for example US-06 or HWFET
for highway fuel economy test. There are cycles that exaggerate the vehicle's
acceleration demands and are known as real world drive cycles.
The drive cycles listed in Table 3.5 showdistinct geographical character. The first
three rows, for example, define the average and maximum speed of how large groups