Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
belt and is most popular as the transmission in subcompact and compact passenger
cars. This type of CVT will exhibit a fuel savings of 8% when compared to a con-
ventional 4-speed automatic transmission. This fuel savings is the same for a 6-speed
automatic transmission, but
the CVT is claimed to offer better acceleration
performance.
The toroidal CVT is better suited to larger passenger vehicles with high dis-
placement engines (400 Nm torque range). Fuel economy in larger cars is improved
because the CVT offers wider gear shift ratio coverage that can push the ICE
farther into its lugging range than a conventional transmission. The limitation of
toroidal CVTs in the past has been the design of the variator, particularly its limited
cross-section space allocation due to vehicle design. Dual cavity toroidal CVTs are
most suitable for rear wheel drive vehicles, hence larger passenger cars, light trucks
and sports utility vehicles. Low variator efficiency occurs when there is excessive
contact pressure on the torus rollers in the low ratio position and when large ratio
spreads are demanded. Efficiency at ratio spreads greater than 5.6:1 can fall from
94% to 89% at full load.
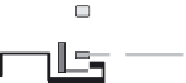
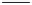
A novel dual cavity, toroidal CVT has been announced by Torotrak and is
called the IVT (infinitely variable transmission) [19] shown in Figure 2.27.
ICE
Wheel
Low
clutch
High
clutch
Figure 2.27 Torotrak IVT, toroidal CVT architecture and production model
In the Torotrak IVT with epicyclic gearing, the system has high and low oper-
ating regimes. In the low regime, the IVT covers low speed, reverse and neutral. In
the high operating regime, the IVT covers all forward speeds including overdrive.
2.3.4 Integrated hybrid assist transmission
The transmission manufacturer JATCO developed a hybrid automatic transmission
termed integrated hybrid assist transmission (IHAT) that works on the epicyclic
gear principle of speed summing. Rather than employing dual M/Gs for power split
operation, the IHAT uses a single M/G in a unique architecture. Figure 2.28