Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
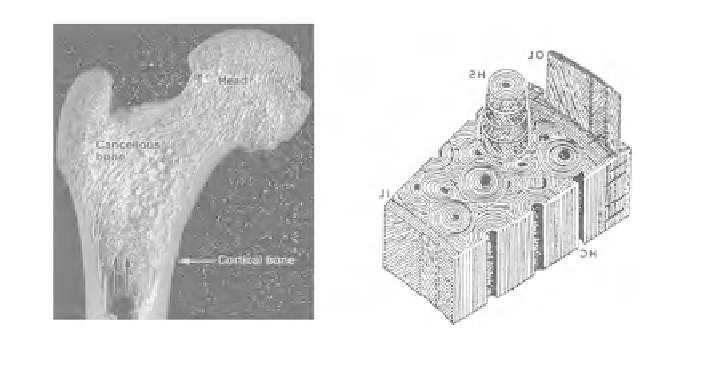
Osteonal
lamellae
Periosteal
lamellae
Osteon
Interstitial
tissue
Cortical
bone
Endosteal
lamellae
Haversian
canal
Fig. 1
Hierarchical
structure
of
cortical
bone
that
is
composed
of
lamellae,
osteon,
and
interstitial tissues
The mineral crystals in bone are plate-like in shape and quite small, having the
length, width, and thickness of 50 9 25 nm 9 *1.5-4.0 nm, respectively [
9
-
11
].
Early X-ray diffraction studies indicate that the bone mineral is similar to
hydroxyapatite, Ca
5
(PO
4
)
3
(OH) [
12
,
13
], but with some distinctions compared
to synthetic hydroxyapatite [
14
]. Such distinctions are usually considered due to
non-stoichiometric ratio of calcium to phosphorous, presence of strongly bound
water, and deposition of amorphous mineral (tricalcium or octacalcium phosphate)
[
8
]. Some studies suggest that the mineral phase may be classified as a carbonated
apatite Ca
5
(PO
4
CO
3
)
3
since hydroxyl groups are not observed when bone is
analyzed
with
Fourier
Transform
Infrared
Spectroscopy
(FTIR)
or
Nuclear
Magnetic Resonance (NMR) [
15
,
16
].
2.1.2 Organic Matrix
The organic matrix consists of collagen and non-collagenous proteins, with type I
collagen being the major part ([90%). Secreted by bone forming cells known as
osteoblasts, procollagen is a triple helical rod of three intertwining polypeptide
chains (two identical a1 helices and one different a2 helix), each containing
approximately 1,000 amino acids, in which every third residue is glycine and
positioned toward the center of the super-coil [
17
]. Proline typically occupies the
next position, and there is an abundance of hydroxyproline in the third position.
Hydroxylysine is a unique residue of bone collagen and gives rise to cross-linking.
Upon enzymatic cleavage of the non-helical, amino (N) and carboxyl (C)
terminals, procollagen forms collagen fibrils by self-assembling via crosslinks
into a staggered arrangement. In general, collagen fibrils are 30-80 nm in
diameter [
18
]. There are no data currently available regarding the length distri-
bution of collagen fibrils in bone. However, it is anticipated that they are longer




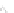










Search WWH ::

Custom Search