Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
effect of certain pharmaceuticals. A comparative AFM study of the membrane
protein organization in native and cataract-affected eye lens membranes
allowed to extend our knowledge about the molecular bases of cataract in an
individual patient and to highlight the potential of AFM as a future medical
imaging tool.
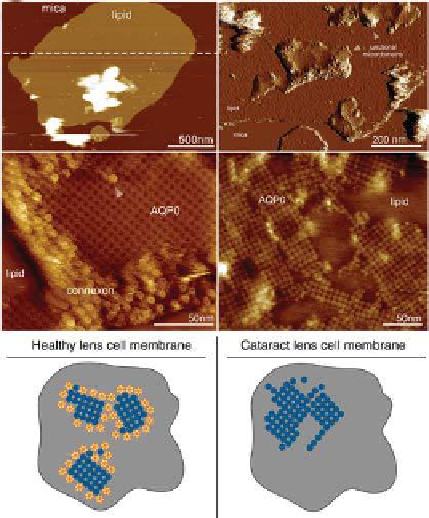
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
Figure 2.8
. Junctional microdomains in lens membranes from healthy and cataract-
affected eye lenses. (a) AFM image of a lens ibre cell membrane fragment on mica
surface. The membrane thickness measured along the dashed line is about 4.5 nm.
(b) The extracellular face of junctional microdomains (marked by arrows). (c) High-
resolution AFM image of a junctional microdomain. Aquaporin-0 (AQP0)-formed
2D arrays edged by closed packed connexons. (d) AFM topograph of a junctional
microdomain from a cataract-affected eye lens. AQP0 constituted malformed arrays
and connexon domains were absent. (e) Models of the supramolecular assembly of
junctional microdomains in lens core cell membranes (
cataract-
affected). In the healthy case, AQP0 form square arrays edged by connexons, providing
water and metabolite transport together, and cell adhesion. In the pathological case,
connexons were absent and AQP0 assemble in larger and continuous but less-ordered
domains. Failure of the lens microcirculation causes clouding of the lens.
left:
healthy;
right:
Eye lens membranes originating from patients with senile cataract and
type II diabetes-induced cataract have been studied.
75,76
In both cases, the
membranes contained larger and less structured AQP0 domains arrays















Search WWH ::

Custom Search