Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
degradation causes further serious damage to both the nuclear envelope and
the cell nucleus. The nuclear lamina confers crucial structural and mechanical
stability to the whole nucleus and is directly involved in the regulation of
gene expression. Mutations in the nuclear lamina are known to lead to severe
diseases (laminopathies).
45
All in all, degradation of the NPC basket and the
nuclear lamina disrupts the essential cross-talk between the chromatin and
the nuclear envelope as well as between the nucleo- and cytoplasma. Nuclear
lamina degradation also leads to nuclear envelope softening, which ultimately
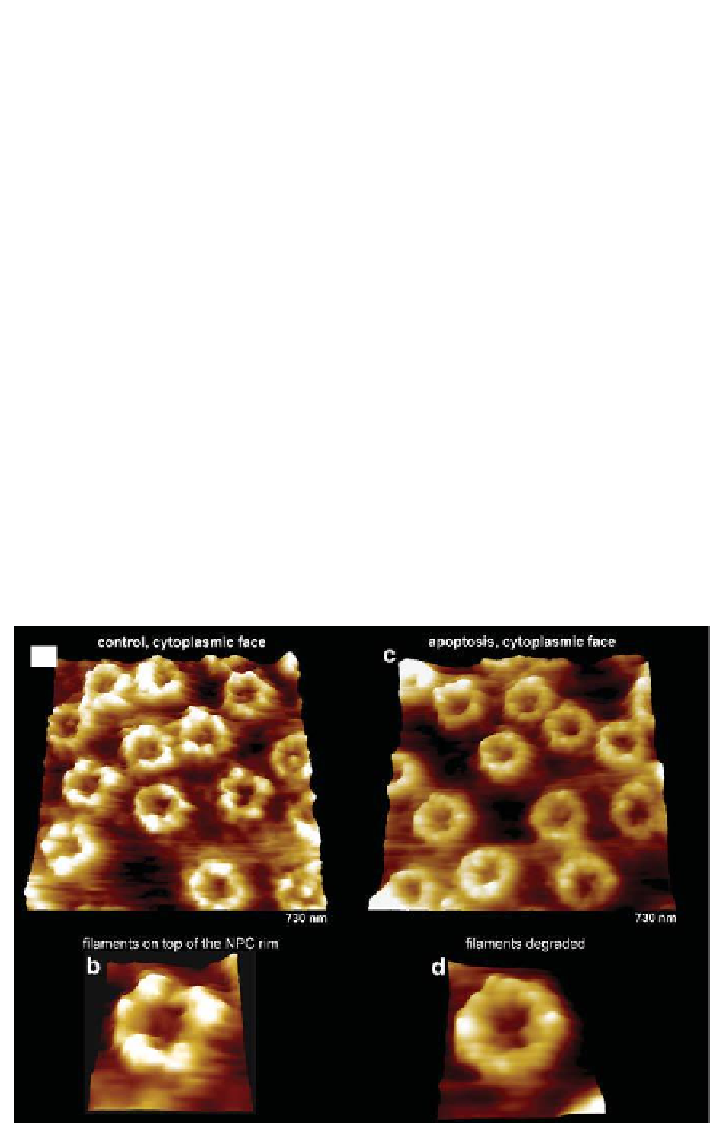
6.3.4.2 The cytoplasmic face of the doomed nuclear envelope is
deprived of its prominent structural and funconal features,
the NPC filaments
With respect to the fact that the cytolplasmic NPC ilaments are essential for
import of proteins from the cytosol into the nucleus, the consequence of their
degradation is impaired nucleocytoplasmic cross-talk and a loss of nuclear
import selectivity. This in turn promotes the nuclear access of generally
excluded cytosolic apoptotic factors.
(c)
(a)
(b)
(d)
Figure 6.19.
AFM images of the cytoplasmic faces of control (left) versus apoptotic
(right) nuclear envelopes of
Xenopus l.
oocyte.
42
















Search WWH ::

Custom Search