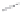Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 1.14
Artificial
intelligence
The Major Elements of Artificial
Intelligence
Vision
systems
Learning
systems
Robotics
Expert systems
Neural networks
Natural language
processing
Expert Systems
Expert systems
give the computer the ability to make suggestions and function like an expert
in a particular field, helping enhance the performance of the novice user. The unique value
of expert systems is that they allow organizations to capture and use the wisdom of experts
and specialists. Therefore, years of experience and specific skills are not completely lost when
a human expert dies, retires, or leaves for another job. Expert systems can be applied to almost
any field or discipline. They have been used to monitor nuclear reactors, perform medical
diagnoses, locate possible repair problems, design and configure IS components, perform
credit evaluations, and develop marketing plans for a new product or investment strategy.
The collection of data, rules, procedures, and relationships that must be followed to achieve
value or the proper outcome is contained in the expert system's
knowledge base
.
expert system
A system that gives a computer the
ability to make suggestions and
function like an expert in a particu-
lar field.
knowledge base
The collection of data, rules, proce-
dures, and relationships that must
be followed to achieve value or the
proper outcome.
Virtual Reality
Virtual reality
is the simulation of a real or imagined environment that can be experienced
visually in three dimensions. Cigna Healthcare, for example, is experimenting with a virtual
HopeLab (
www.hopelab.org
)
, the virtual reality game called Re-Mission shows young adults
and children how to combat cancer.
Originally, virtual reality referred to immersive virtual reality, which means the user
becomes fully immersed in an artificial, computer-generated 3-D world. The virtual world
is presented in full scale and relates properly to the human size. Virtual reality can also refer
to applications that are not fully immersive, such as mouse-controlled navigation through a
3-D environment on a graphics monitor, stereo viewing from the monitor via stereo glasses,
stereo projection systems, and others. Boeing, for example, used virtual reality and computer
Boeing's vice president of process integration, “A breakthrough program like the 787
Dreamliner needed to lead the way in performance, quality, cost, and schedule supported
by efficient and effective production planning.” Boeing used 3-D models from Dassault
Systems to design and manufacture the new aircraft. Retail stores like Saks Fifth Avenue
and Neiman-Marcus are using virtual reality to help advertise high-end products on the
were received in less than a week.
A variety of input devices, such as head-mounted displays (see Figure 1.15), data gloves,
joysticks, and handheld wands, allow the user to navigate through a virtual environment and
to interact with virtual objects. Directional sound, tactile and force feedback devices, voice
recognition, and other technologies enrich the immersive experience. Because several people
can share and interact in the same environment, virtual reality can be a powerful medium
for communication, entertainment, and learning.
virtual reality
The simulation of a real or imagined
environment that can be experi-
enced visually in three dimensions.