Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
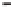
Table 11.2
Ability to
Natural Intelligence
(Human)
Artificial Intelligence
(Machine)
A Comparison of Natural and
Artificial Intelligence
Low
High
Low
High
√
√
Use sensors (eyes, ears,
touch, smell)
√
√
Be creative and imaginative
√
√
Learn from experience
√
√
Adapt to new situations
√
√
Afford the cost of acquiring
intelligence
√
√
Acquire a large amount of
external information
√
√
Use a variety of information
sources
√
√
Make complex calculations
√
√
Transfer information
Make a series of calculations
rapidly and accurately
√
√
Figure 11.5
Artificial
intelligence
A Conceptual Model of Artificial
Intelligence
Vision
systems
Learning
systems
Robotics
Expert systems
Neural networks
Natural language
processing
mechanical devices that don't use the AI features discussed in this chapter. Others are
sophisticated systems that use one or more AI features or characteristics, such as vision sys-
tems, learning systems, or neural networks discussed later in the chapter. For many businesses,
robots are used to do the three Ds—dull, dirty, and dangerous jobs. Manufacturers use
people to recommend using robots instead of people to explore space and perform scientific
research. Some robots, such as the ER series by Intelitek (
www.intelitek.com
),
can be used for
training or entertainment. Contemporary robotics combine both high-precision machine