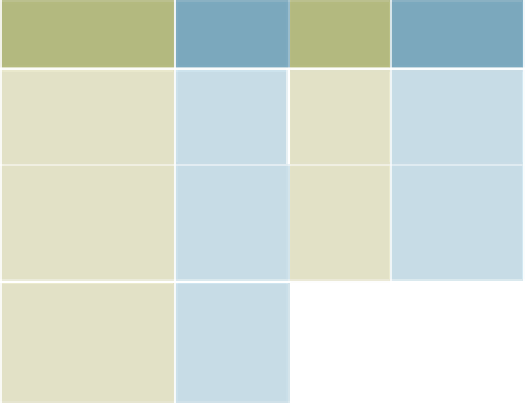Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
connection, you must have an account with the service provider and software that allows a
direct link via TCP/IP.
For a dial-up connection, ISPs typically charge a monthly fee that can range from $10
to $30 for unlimited Internet access. The fee normally includes e-mail. Many ISPs and online
services offer broadband Internet access through DSLs, cable, or satellite transmission.
Broadband users pay between $30 and $60 per month for unlimited service. Broadband rates
differ based on the speed of the connection. Some businesses and universities use the very
fast T1 or T3 lines to connect to the Internet. T1 and T3 support high data rates, but have
additional value over DSL and cable because they can send many signals simultaneously.
Table 7.3 compares the speed of modem, DSL, cable, and T1 Internet connections to perform
basic tasks. This table uses advertised connection speeds; your performance will be slower.
These technologies were discussed in Chapter 6.
Table 7.3
T3 (44
Mbps)
Task
Modem
(56Kbps)
T1 (1.4
Mbps)
DSL (3
Mbps)
Cable (7
Mbps)
Approximate Times to Perform
Basic Tasks at Advertised
Connection Speeds
Send 20-page
term paper
(500 KB)
9 seconds
0.36
seconds
0.17
seconds
.07 seconds
.01 seconds
Send a four-
minute song as
an MP3 file (4.5
MB)
80
seconds
3.2
seconds
1.5 seconds
.64 seconds
0.1 seconds
Send a full-length
motion picture as
a compressed file
(1.4 GB)
About 7
hours
About 16
minutes
7.8 minutes
3.3 minutes
.53 seconds
Some ISPs are experimenting with low-fee or no-fee Internet access, though strings are
attached to the no-fee offers in most cases. Some free ISPs require that customers provide
detailed demographic and personal information. In other cases, customers receive extra ad-
vertising when using the Web. For example, a
pop-up ad
is a window that is displayed when
someone visits a Web site. It opens and advertises a product or service. Some e-commerce
retailers have posted ads that resemble computer-warning messages and have been sued for
deceptive advertising. A
banner ad
appears as a banner or advertising element within a Web
site's layout, which you can ignore or click to go to the advertiser's Web site.