Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Service
A
digital subscriber line (DSL)
is a telecommunications service that delivers high-speed
Internet access to homes and small businesses over the existing phone lines of the local tele-
phone network (see Figure 6.14). Most home and small business users are connected to an
asymmetric DSL (ADSL)
line designed to provide a connection speed from the Internet to
the user (download speed) that is three to four times faster than the connection from the user
back to the Internet (upload speed). ADSL does not require an additional phone line and
yet provides “always-on” Internet access. A drawback of ADSL is that the farther the sub-
scriber is from the local telephone office, the poorer the signal quality and the slower the
transmission speed. ADSL provides a dedicated connection from each user to the phone
company's local office, so the performance does not decrease as new users are added. Cable
modem users generally share a network loop that runs through a neighborhood so that adding
users means lowering the actual transmission speeds.
Symmetric DSL (SDSL)
is used mainly
by small businesses and does not allow you to use the phone at the same time, but the speed
of receiving and sending data is the same.
digital subscriber line (DSL)
A telecommunications service that
delivers high-speed Internet access
to homes and small businesses over
the existing phone lines of the local
telephone network.
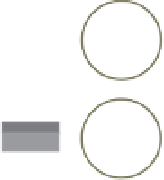
Figure 6.14
Telephone
Fax
Telephone
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
At the local telephone company's
central office, a DSL Access
Multiplexer (DSLAM) takes
connections from many customers
and multiplexes them onto a single,
high-capacity connection to the
Internet. Subscriber phone calls can
be routed through a switch at the
local telephone central office to the
public telephone network.
Central office
Public
telephone
network
Switch
DSL
Modem
DSLAM
ISP
Internet
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) Services
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
is a collection of technologies and communications
protocols that enables voice conversations to be converted into packets of data that can be
sent over a data network such as the Internet, a WAN, or a LAN. You can use VoIP to make
a call directly from a computer equipped with appropriate software and a microphone, a
special VoIP phone, or an ordinary phone connected to an analog telephone adapter that
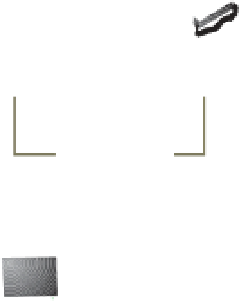
converts the analog voice signal into data packets (see Figure 6.15).
Voice over Internet Protocol
(VoIP)
A collection of technologies and
communications protocols that
enables your voice to be converted
into packets of data that can be sent
over a data network such as the
Internet, a WAN or LAN.
Personal
Computer
Figure 6.15
Telephone
VoIP Options
VoIP
Phone
Phone
Adapter
Cable
Modem
Internet
Telephone
Personal
Computer