Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
department implemented a MAN to enable its officers to gain easy access to the data they
need while staying mobile on the streets rather than behind a desk. Officers in cruisers connect
to hot spots in station parking lots to gain access to the network. Here they can download
reports and access local and national databases for fingerprints, mug shots, and other infor-
mation about suspects. Officers can also participate in pretrial meetings via videoconferencing
at their district stations and save the hours required to go downtown and meet face-to-face
with prosecutors and others. Bob Reyes, the systems support manager, says: “We're in the
midst of a five-year plan. Much of what that involves is putting computers into the cars and
providing our officers with timely upgrades, patches, and virus controls through wireless
connectivity when they enter their district station areas without having to go inside or wait
in line to plug into the network.”
36
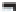
Wide area networks
A
wide area network (WAN)
is a telecommunications network that connects large geographic
regions. A WAN might be privately owned or rented and includes public (shared users)
networks. When you make a long-distance phone call or access the Internet, you are using a
WAN. WANs usually consist of computer equipment owned by the user, together with data
communications equipment and telecommunications links provided by various carriers and
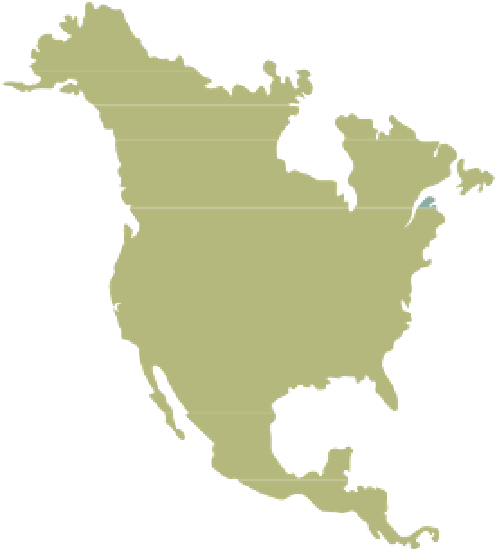
service providers (see Figure 6.7).
wide area network (WAN)
A telecommunications network that
ties together large geographic
regions.
Figure 6.7
A Wide Area Network
WANs are the basic long-distance
networks used around the world.
The actual connections between
sites, or nodes (shown by dashed
lines), might be any combination of
guided and wireless media. When
you make a long-distance telephone
call or access the Internet, you are
using a WAN.
North America
WANs often provide communications across national borders, which involves national
and international laws regulating the electronic flow of data across international boundaries,
often called
transborder data flow
. Many countries, including those in the European Union,
have strict laws limiting the use of telecommunications and databases, making normal busi-
ness transactions such as payroll costly, slow, or even impossible.
Basic Processing Alternatives
When an organization needs to use two or more computer systems, it can implement one of
three basic processing alternatives: centralized, decentralized, or distributed. With
centralized
processing
, all processing occurs in a single location or facility. This approach offers the
highest degree of control because a single centrally managed computer performs all data
centralized processing
Processing alternative in which all
processing occurs at a single loca-
tion or facility.