Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
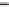
A communications satellite also operates in the microwave frequency range (see Figure
6.5). The satellite receives the signal from the Earth station, amplifies the relatively weak
signal, and then rebroadcasts it at a different frequency. The advantage of satellite commu-
nications is that it can receive and broadcast over large geographic regions. Such problems
as the curvature of the Earth, mountains, and other structures that block the line-of-
sight microwave transmission make satellites an attractive alternative. Geostationary, low
earth orbit, and small mobile satellite stations are the most common forms of satellite
communications.
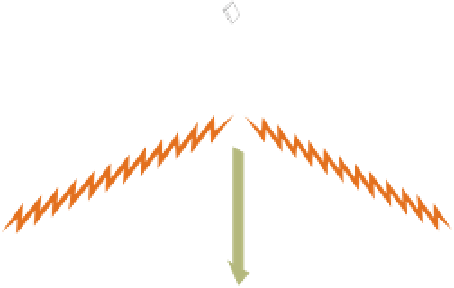
Figure 6.5
Communications
satellite
Satellite Transmission
Communications satellites are relay
stations that receive signals from
one Earth station and rebroadcast
them to another.
Microwave
station
Microwave
station
Approximately
22,000
miles
Earth
A
geostationary satellite
orbits the Earth directly over the equator, approximately 22,300
miles above the Earth so that it appears stationary. The U.S. National Weather Service relies
on the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite program for weather imagery and
quantitative data to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking, and meteorological
research.
A
low earth orbit (LEO) satellite
system employs many satellites, each in an orbit at an
altitude of less than 1,000 miles. The satellites are spaced so that, from any point on the Earth
at any time, at least one satellite is on a line of sight.
A
very small aperture terminal (VSAT)
is a satellite ground station with a dish antenna
smaller than 3 meters in diameter. News organizations employ VSAT dishes that run on
battery power to quickly establish communications and transmit news stories from remote
locations. Many people are also investing in VSAT technology in their homes to receive TV
and send and receive computer communications.
Kerr-McGee is the largest independent oil producer and leaseholder in the deep waters
of the Gulf of Mexico. The firm implemented a VSAT-based communications system to
enable drilling rig crews to communicate reliably with each other, the main office, and friends
and family back home. The network can also be used to share data and video of underwater
pipelines with technical experts at headquarters and regional offices so that faster and better
operational decisions can be made.
21
Wireless Mesh
Wireless mesh
uses multiple Wi-Fi access points to link a series of interconnected local area
networks to form a wide area network capable of serving a large campus or entire city. Com-
munications are routed among network nodes by allowing for continuous connections and
reconfiguration around blocked paths by “hopping” from node to node until a connection
can be established. Mesh networks are very robust: If one node fails, all the other nodes can
still communicate with each other, directly or through one or more intermediate nodes.
wireless mesh
A way to route communications
between network nodes (computers
or other devices) by allowing for
continuous connections and recon-
figuration around blocked paths by
“hopping” from node to node until a
connection can be established.