Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
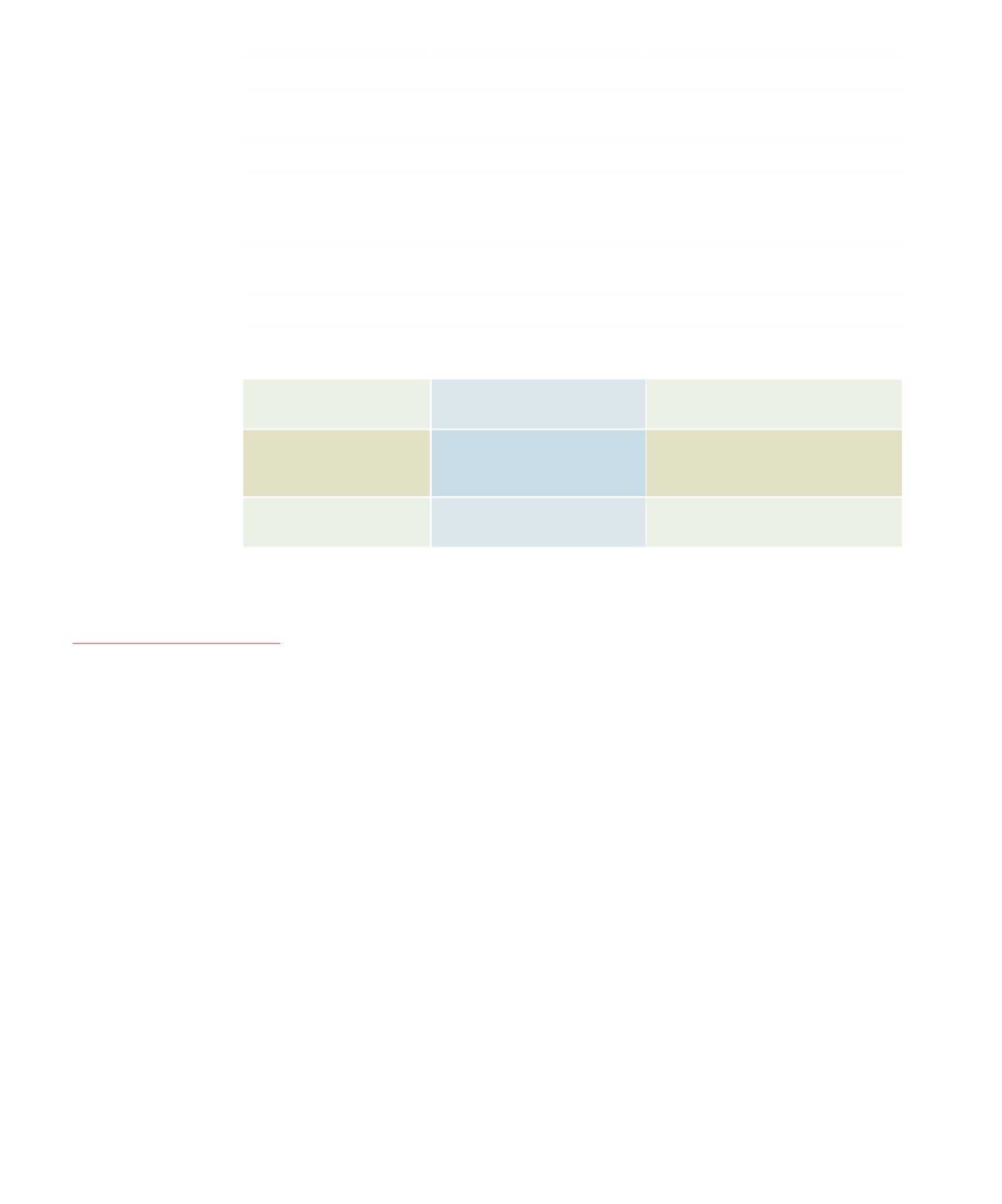
Characteristic
OLTP Database
Data Warehousing
Support decision making
Purpose
Support transaction processing
Source of data
Business transactions
Multiple files, databases—data
internal and external to the firm
Data access allowed users
Read and write
Read only
Primary data access mode
Simple database update
and query
Simple and complex database queries
with increasing use of data mining to
recognize patterns in the data
Primary database model
employed
Relational
Relational
Level of detail
Detailed transactions
Often summarized data
Availability of historical
data
Very limited—typically a few
weeks or months
Multiple years
Update process
Online, ongoing process as
transactions are captured
Periodic process, once per week
or once per month
Ease of process
Routine and easy
Complex, must combine data from
many sources; data must go
through a data cleanup process
Data integrity issues
Each transaction must be
closely edited
Major effort to “clean” and integrate
data from multiple sources
Table 5.7
Data Mining
Data mining
is an information-analysis tool that involves the automated discovery of patterns
and relationships in a data warehouse. Like gold mining, data mining sifts through mountains
of data to find a few nuggets of valuable information. The University of Maryland has de-
system uses a real-time data extraction tool called T-REX to scour an average of 128,000
articles a day and forecast future activities of over 110 terrorist groups.
Data mining's objective is to extract patterns, trends, and rules from data warehouses to
evaluate (i.e., predict or score) proposed business strategies, which will improve competi-
tiveness, increase profits, and transform business processes. It is used extensively in marketing
to improve customer retention; cross-selling opportunities; campaign management; market,
channel, and pricing analysis; and customer segmentation analysis (especially one-to-one
marketing). In short, data-mining tools help users find answers to questions they haven't
thought to ask.
E-commerce presents another major opportunity for effective use of data mining. At-
tracting customers to Web sites is tough; keeping them can be next to impossible. For
example, when retail Web sites launch deep-discount sales, they cannot easily determine how
many first-time customers are likely to come back and buy again. Nor do they have a way of
understanding which customers acquired during the sale are price sensitive and more likely
to jump on future sales. As a result, companies are gathering data on user traffic through their
Web sites and storing the data in databases. This data is then analyzed using data-mining
techniques to personalize the Web site and develop sales promotions targeted at specific
customers.
Predictive analysis
is a form of data mining that combines historical data with assump-
tions about future conditions to predict outcomes of events, such as future product sales or
the probability that a customer will default on a loan. Retailers use predictive analysis to
upgrade occasional customers into frequent purchasers by predicting what products they will
buy if offered an appropriate incentive. Genalytics, Magnify, NCR Teradata, SAS Institute,
Comparison of OLTP and Data
Warehousing
data mining
An information-analysis tool that
involves the automated discovery of
patterns and relationships in a data
warehouse.
predictive analysis
A form of data mining that combines
historical data with assumptions
about future conditions to predict
outcomes of events, such as future
product sales or the probability that
a customer will default on a loan.