Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
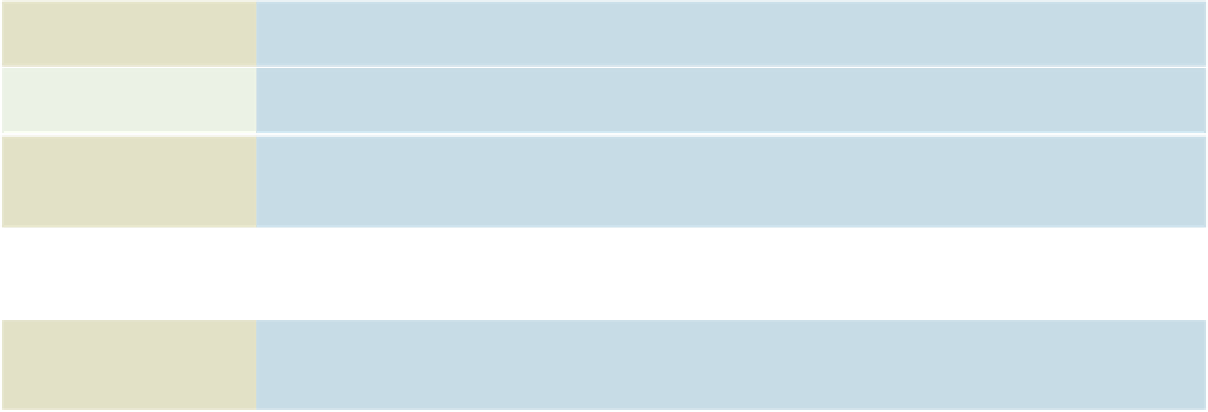
Advantages
Explanation
Improved strategic use
of corporate data
Accurate, complete, up-to-date data can be made available to decision makers where, when, and in the form
they need it. The database approach can also give greater visibility to the organization's data resource.
Reduced data
redundancy
Data is organized by the DBMS and stored in only one location. This results in more efficient use of system
storage space.
Improved data integrity
With the traditional approach, some changes to data were not reflected in all copies of the data kept in
separate files. The database approach prevents this problem because no separate files contain copies of the
same piece of data.
Easier modification and
updating
The DBMS coordinates data modifications and updates. Programmers and users do not have to know where
the data is physically stored. Data is stored and modified once. Modification and updating is also easier
because the data is commonly stored in only one location.
Data and program
independence
The DBMS organizes the data independently of the application program, so the application program is not
affected by the location or type of data. Introduction of new data types not relevant to a particular application
does not require rewriting that application to maintain compatibility with the data file.
Better access to data
and information
Most DBMSs have software that makes it easy to access and retrieve data from a database. In most cases,
users give simple commands to get important information. Relationships between records can be more
easily investigated and exploited, and applications can be more easily combined.
Standardization of data
access
A standardized, uniform approach to database access means that all application programs use the same
overall procedures to retrieve data and information.
A framework for
program development
Standardized database access procedures can mean more standardization of program development.
Because programs go through the DBMS to gain access to data in the database, standardized database
access can provide a consistent framework for program development. In addition, each application program
need address only the DBMS, not the actual data files, reducing application development time.
Better overall
protection of the data
Accessing and using centrally located data is easier to monitor and control. Security codes and passwords
can ensure that only authorized people have access to particular data and information in the database, thus
ensuring privacy.
Shared data and
information resources
The cost of hardware, software, and personnel can be spread over many applications and users. This is a
primary feature of a DBMS.
Table 5.1
Disadvantages
Explanation
Advantages of the Database
Approach
DBMSs can be difficult to set up and operate. Many decisions must be
made correctly for the DBMS to work effectively. In addition, users have
to learn new procedures to take full advantage of a DBMS.
More complexity
With the traditional approach to file management, a failure of a file
affects only a single program. With a DBMS, a failure can shut down
the entire database.
More difficult to
recover from a failure
DBMSs can be more expensive to purchase and operate. The expense
includes the cost of the database and specialized personnel, such as
a database administrator, who is needed to design and operate the
database. Additional hardware might also be required.
Table 5.2
More expensive
Disadvantages of the Database
Approach
Many modern databases serve entire enterprises, encompassing much of the data of the
organization. Often, distinct yet related databases are linked to provide enterprise-wide
databases. For example, many Wal-Mart stores include in-store medical clinics for customers.
Wal-Mart uses a centralized electronic health records database that stores the information of
to provide information about customers' interactions with the clinics and stores. The Ethical
and Societal Issues box provides more information about databases used for electronic
health record systems.